2016 Senior Design Projects
Multi-Axis Prosthetic (MAP) Ankle: Guiding Amputees Towards Independence
SprinGait: Dress to Compress - A New Ankle-Foot Orthotic for Patients with Drop Foot
StrideSmart: Gait Monitoring and Improvement in the Geriatric Population
Smart Assistive Device for the Visually Impaired
EEG Monitoring for Drowsiness Detection while Driving
Saving the Rhino: One Ultrasound at a Time
ProGraft: The Proactive Solution to a Long-Lasting Hemodialysis Graft
Balancing Assistive Device for Peripheral Neuropathy
Keeping an Eye On Contact Lenses
PneuDia: A Portable Pneumonia Sensor Employable in Low Resource Areas
C-EAR – Canine Equipment for Acoustic Research
NID – Nasogastric Intubation Dummy
Multi-Axis Prosthetic (MAP) Ankle: Guiding Amputees Towards Independence
Andre Woloshuk, Mitchell Hoge, Peter Russel, Michael Loke
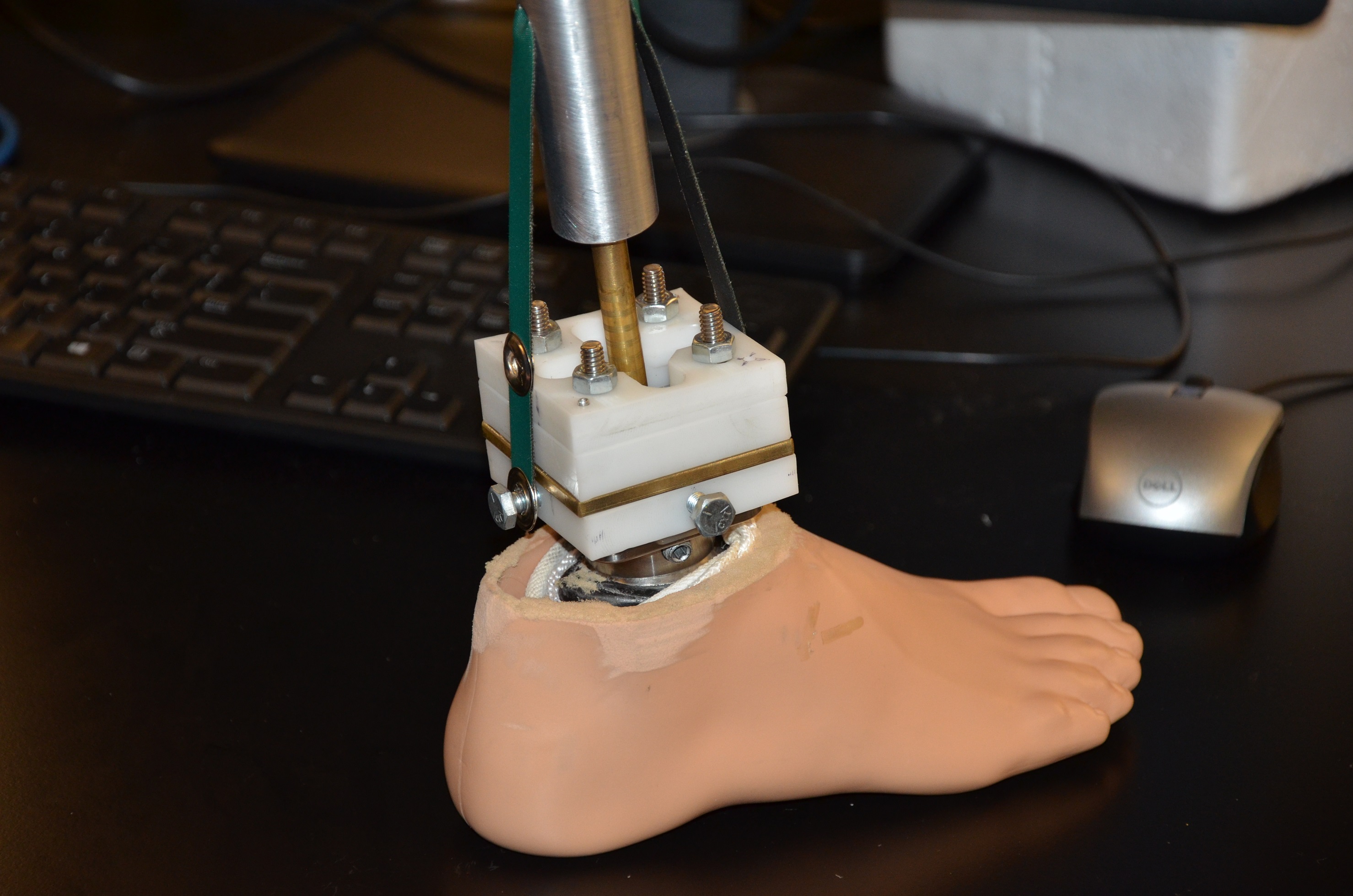 There are an estimated 9.6 million people in developing countries living with the consequences of lower limb amputation. With monthly Guatemalan incomes averaging less than $300, affordable prosthetics lack the necessary stability and flexibility to allow patients to earn a living. There is a need for a comfortable, durable, and locally produced ankle prosthetic for adults in developing countries that provides the same range of motion as the normal human ankle at low-cost and. In order to solve this clinical need, a solution has been developed that can help improve mobility and help lower limb amputees regain independence to support themselves and their families. This unique design restricts the range of motion of the ankle to precise angles for plantarflexion, dorsiflexion, inversion, eversion, adduction, abduction to mimic normal human motion. The solution gives the ankle controlled motion as well as a method for returning the foot to an un-rotated, equilibrium position. Additionally, the design withstands extensive (2 million cycles) repetitive loading. The ankle-foot interface is composed of a four-hole pyramid receiver, which is a standard connecting piece for all prosthetic ankles. This allows the design to be universal to all prosthetic feet. Verification testing has shown this design is able to provide increased flexibility and stability, while remaining low-cost, accessible, and durable for amputees in developing countries. This prosthetic will provide an avenue for amputees to return to work and independent living.
There are an estimated 9.6 million people in developing countries living with the consequences of lower limb amputation. With monthly Guatemalan incomes averaging less than $300, affordable prosthetics lack the necessary stability and flexibility to allow patients to earn a living. There is a need for a comfortable, durable, and locally produced ankle prosthetic for adults in developing countries that provides the same range of motion as the normal human ankle at low-cost and. In order to solve this clinical need, a solution has been developed that can help improve mobility and help lower limb amputees regain independence to support themselves and their families. This unique design restricts the range of motion of the ankle to precise angles for plantarflexion, dorsiflexion, inversion, eversion, adduction, abduction to mimic normal human motion. The solution gives the ankle controlled motion as well as a method for returning the foot to an un-rotated, equilibrium position. Additionally, the design withstands extensive (2 million cycles) repetitive loading. The ankle-foot interface is composed of a four-hole pyramid receiver, which is a standard connecting piece for all prosthetic ankles. This allows the design to be universal to all prosthetic feet. Verification testing has shown this design is able to provide increased flexibility and stability, while remaining low-cost, accessible, and durable for amputees in developing countries. This prosthetic will provide an avenue for amputees to return to work and independent living.
SUPPORT (Sensing unusual poor posture & rehabilitation therapy) - Integrated cervical support and electrical feedback to prevent neck pain for military personnel
Hyukjin Jang, Karen Kukla, Wade Rich
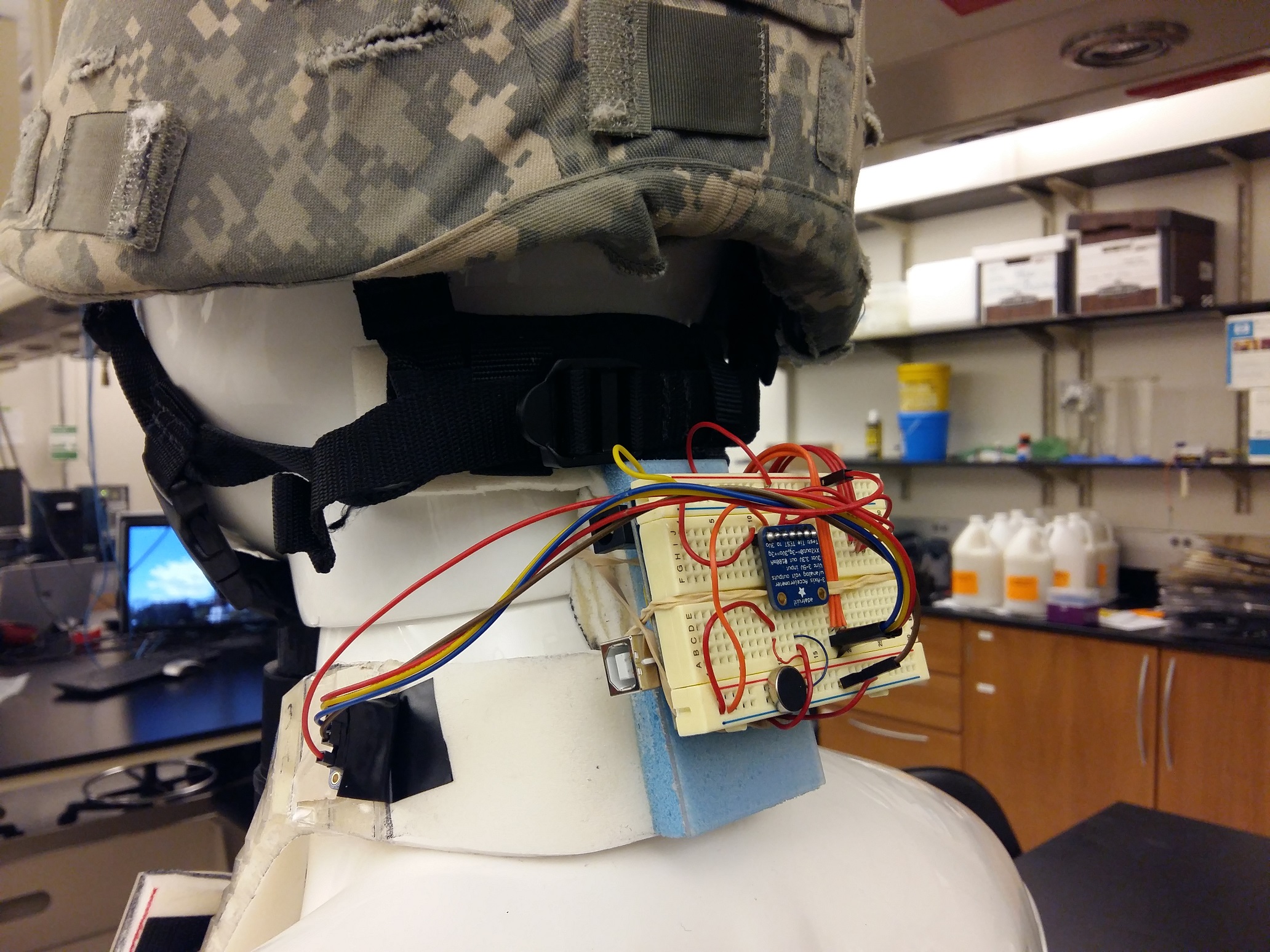 Due to the strenuous activities and cumbersome gear, soldiers overuse their neck muscles, leading to severe neck disorders and pain. From 2003 to 2012, the total number of military patients with neck disorders increased by 129%. The extended straining can result in cervical kyphosis, a disorder in which the natural “C” shape of the neck becomes straight. Cervical kyphosis can cause severe neck pain and negatively impact a soldier’s performance in the field. There is a need for a device that prevents poor neck posture and pain experienced during military service. The proposed solution is a brace that encourages a natural “C” curvature with a chin stabilizer to prevent extreme flexion. Materials used include biocompatible foam and polycarbonate to provide a comfortable yet supporting framework. Two accelerometers detect the user’s craniovertebral angle (CV), which is the angle between a horizontal line through C7 and a line extending from the tragus of the ear to C7. When the angle is outside a desired range, a vibration stimulates the user to correct poor neck posture. The solution is unique because the minimal framework of the device allows for greater mobility than current braces and may prevent neck pain before it occurs. After testing the electrical feedback with various neck angles, the device vibrated with 95% accuracy. For total range of motion (ROM), the device’s average reduction in ROM was 5.75%. This reduction is four times less than the soft foam collar on the current market, indicating an improvement of motility. Since the solution retains a greater percentage of ROM than devices on the market, military personnel can utilize the solution during military activities. Overall, the results suggest the unique combination of the electrical feedback system and supportive will positively impact military personnel's cervical spine health.
Due to the strenuous activities and cumbersome gear, soldiers overuse their neck muscles, leading to severe neck disorders and pain. From 2003 to 2012, the total number of military patients with neck disorders increased by 129%. The extended straining can result in cervical kyphosis, a disorder in which the natural “C” shape of the neck becomes straight. Cervical kyphosis can cause severe neck pain and negatively impact a soldier’s performance in the field. There is a need for a device that prevents poor neck posture and pain experienced during military service. The proposed solution is a brace that encourages a natural “C” curvature with a chin stabilizer to prevent extreme flexion. Materials used include biocompatible foam and polycarbonate to provide a comfortable yet supporting framework. Two accelerometers detect the user’s craniovertebral angle (CV), which is the angle between a horizontal line through C7 and a line extending from the tragus of the ear to C7. When the angle is outside a desired range, a vibration stimulates the user to correct poor neck posture. The solution is unique because the minimal framework of the device allows for greater mobility than current braces and may prevent neck pain before it occurs. After testing the electrical feedback with various neck angles, the device vibrated with 95% accuracy. For total range of motion (ROM), the device’s average reduction in ROM was 5.75%. This reduction is four times less than the soft foam collar on the current market, indicating an improvement of motility. Since the solution retains a greater percentage of ROM than devices on the market, military personnel can utilize the solution during military activities. Overall, the results suggest the unique combination of the electrical feedback system and supportive will positively impact military personnel's cervical spine health.
SprinGait: Dress to Compress - A New Ankle-Foot Orthotic for Patients with Drop Foot
Jake Ditslear, Dana Jablonski, Alexander Shrum, Kelsey Wasilczuk
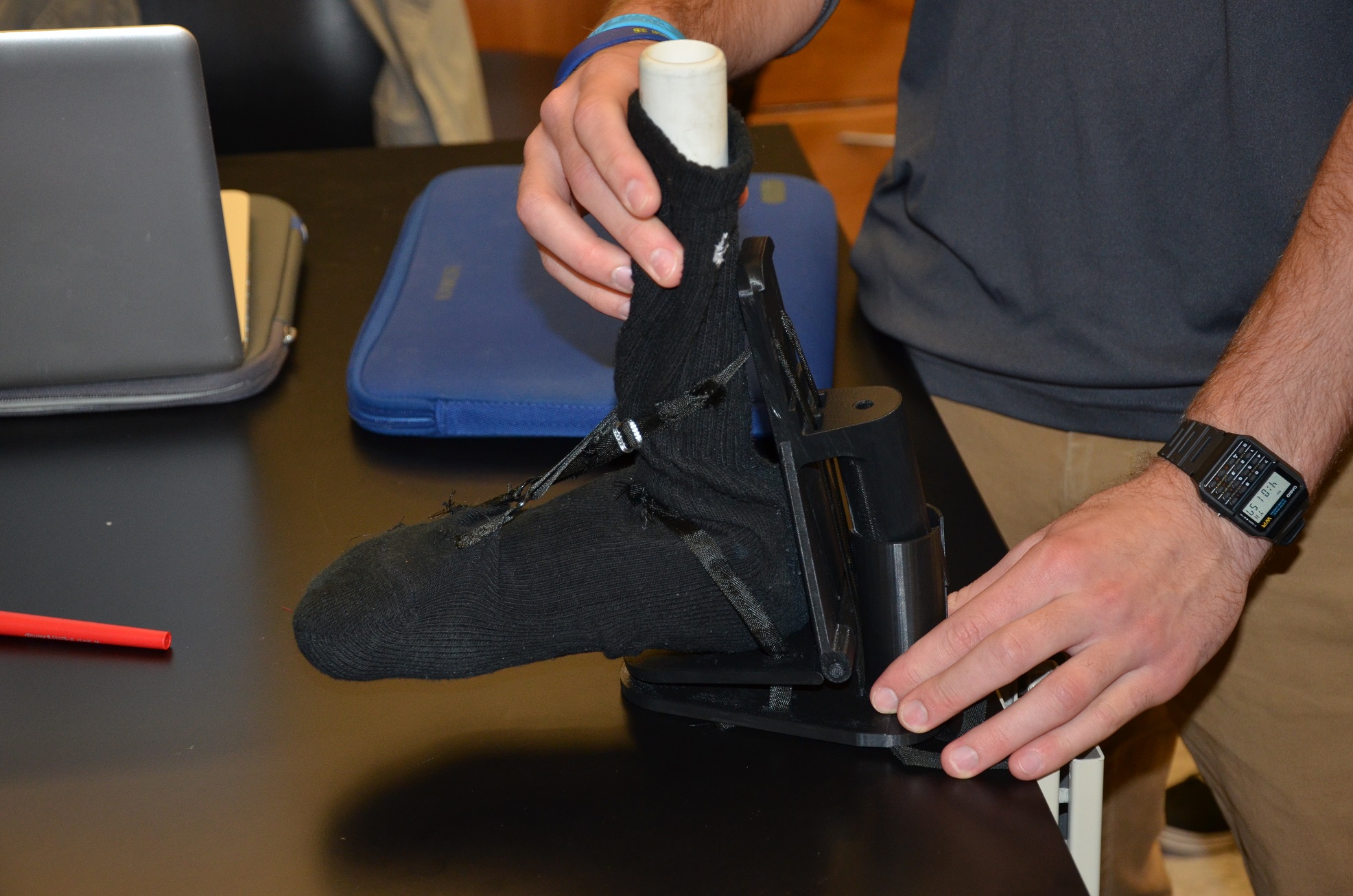 Drop foot is a clinical condition in which a person lacks the ability to perform dorsiflexion (upward lift) and plantarflexion (downward point) of the foot due to neurological or muscular complications. Gait related issues caused by drop foot lead to a higher incidence of falling, slow walking speeds, and decreased confidence. Roughly 45,000 new incidences occur each year as part of 2 million total in the United States. Existing solutions range from Ankle Foot Orthotics (AFOs) to nerve stimulation devices. Existing solutions fail as many are bulky, uncomfortable, or hold the ankle at a fixed angle. There is a need for a new AFO, for all patient types, with a low profile design allowing proper ankle motion during gait.
Drop foot is a clinical condition in which a person lacks the ability to perform dorsiflexion (upward lift) and plantarflexion (downward point) of the foot due to neurological or muscular complications. Gait related issues caused by drop foot lead to a higher incidence of falling, slow walking speeds, and decreased confidence. Roughly 45,000 new incidences occur each year as part of 2 million total in the United States. Existing solutions range from Ankle Foot Orthotics (AFOs) to nerve stimulation devices. Existing solutions fail as many are bulky, uncomfortable, or hold the ankle at a fixed angle. There is a need for a new AFO, for all patient types, with a low profile design allowing proper ankle motion during gait.
SprinGait capitalizes on a compression system utilizing weight transfer to lift the toe during the swing phase. SprinGait is novel in that it is placed behind the heel and exploits the natural shift of body weight on the foot during gait with appropriate timing. It features easy to assemble and adjustable tension straps for patient preference.
SprinGait can be used to effectively correct gait by means of lifting the foot at least 10° in dorsiflexion and 15° in plantarflexion, an adequate range of movement, unlike existing solutions.
Maximum ranges of dorsiflexion and plantarflexion are 20° and 50°, respectively. Given its estimated low manufacturing cost of $50, the user’s ability to set up in under 60 seconds without instruction, and its compatibility with any shoe, this device improves on current market solutions, which average around $200-600.
Compared to fixed AFOs, the purely mechanical SprinGait is a viable alternative allowing the user to simulate a more natural gait. By providing the ability to actuate proper ankle motion, SprinGait is a cost-effective solution for drop foot in everyday use.
StrideSmart: Gait Monitoring and Improvement in the Geriatric Population
Alex Baker, Chloe Beach, Anjali Malik, Raj Patel
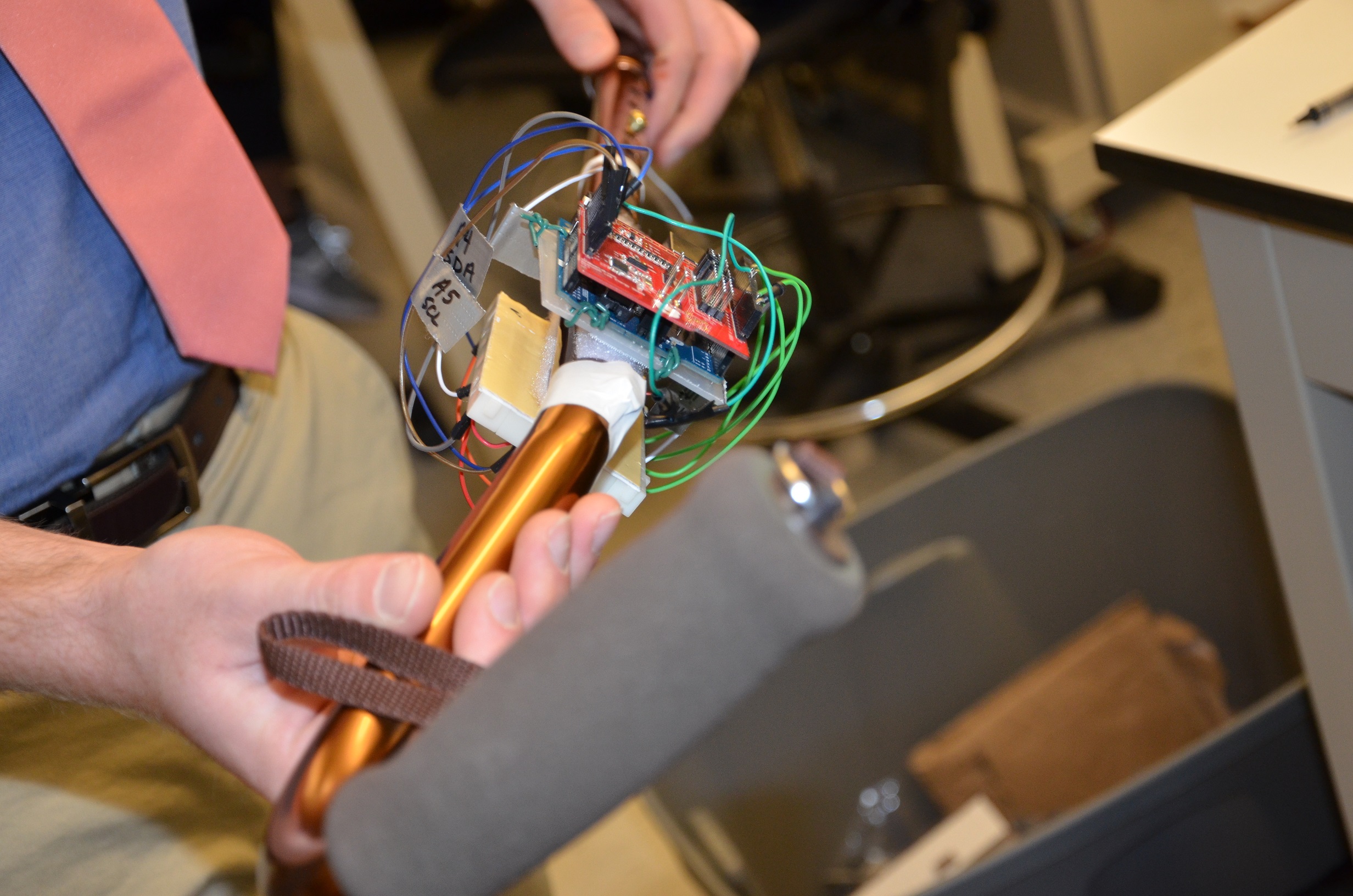
By the year 2040, it is expected that over 21.7% of the U.S. population will be over the age of 65. As of 2015, 1 in 3 people over this age has experienced a fall. Within this population, the number of people who experience a fall continues to increase, leading to varying degrees of injury, loss of independence, fear of future falls, and sedentary lifestyles. Current solutions on the market such as medication or mobility assistive devices attempt to reduce fall occurrence, but do not actively protect the user from falling or monitor walking performance. The geriatric population needs a fall prevention solution that provides immediate feedback and training based on measured data. Caregivers, families, and physicians should also be provided with performance reports and data that quantify the patient’s activities and walking quality. This allows the user’s treatments to be tailored to their current progress by their physicians so that continuous improvement can be seen in their stability and gait patterns. Our team has developed StrideSmart, which consists of attachments for single-tip canes that can quantify the user’s gait patterns and activity levels, as well as provide immediate feedback for gait correction. An iOS application also provides displayable data and alerts to deliver essential information to the user and healthcare providers which can help supply individualized care to support proper walking mechanics and habits. These attachments are expected to successfully train the user to walk with the proper mechanics, provide valuable information to healthcare providers, and promote a healthy, active, and confident lifestyle for the geriatric patient.
Smart Assistive Device for the Visually Impaired
Bahar Dhowan, Steven Oleson, Siddharth Prabhu, Sarah Septiani
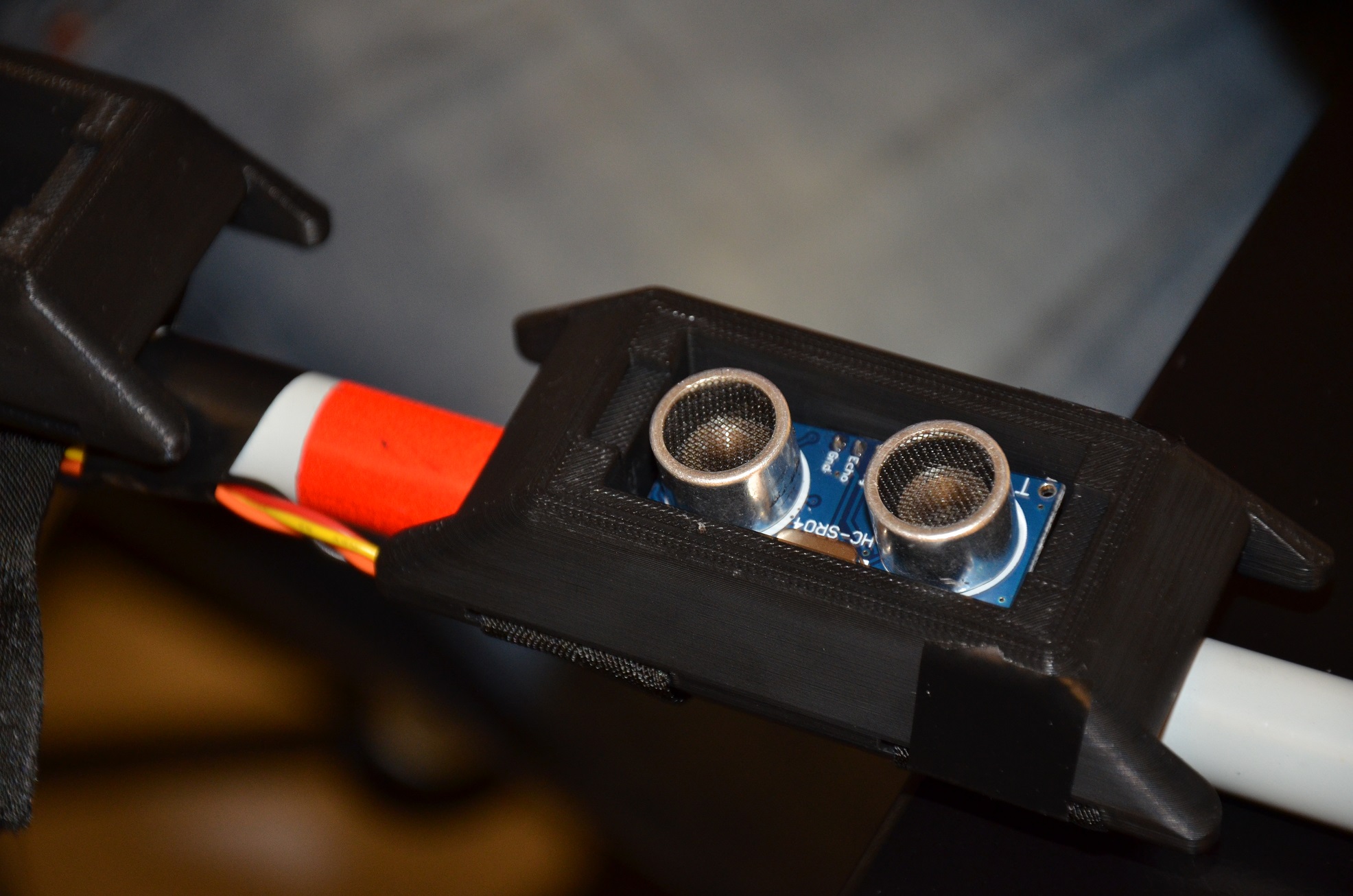

Vision loss is defined as a permanent visual impairment that is not correctable with spectacles or contact lenses, consequently causing lowered mobility and self-navigation. There are 285 million people who suffer from visual impairments worldwide and 80% of this population are unable to afford the cost of treatment. Currently, the long cane is the primary mobility tool used by people suffering from visual impairments, but it does not detect objects above the waist. Our team has designed a cost-effective, smart assistive device that is attachable to the long cane and seeks to address this problem. The prototype was tested by placing objects at various distances away from the user and allowing the user to navigate around the objects with our device. The results were interpreted by determining sensitivity and specificity values, 90% and 94% respectively. These values indicated that the device was successfully able to detect objects. Human subject testing was also used to ensure that the user can learn the device in a timely manner. In conclusion, the smart assist device was able to detect objects with a confidence of 95% and was successful in improving the navigation of unknown environments for the visually impaired population.
Early Stroke Detection
Melissa Ullmer, Michael Duarte, Courtney Judson, Avik Maewall, McCaela Moes
A stroke is a term used to designate any obstruction of blood flow that causes oxygen deprivation of any part of the brain, resulting in the death of 120 million neurons per hour [4]. The most common site of strokes is the middle cerebral artery, which supplies portions of the brain responsible for controlling the arms, legs, face, balance, and speech.
Every year, nearly 60,000 of 790,000 total strokes go unnoticed causing permanent damage. A device is needed that quickly identify potential strokes and aid the user in securing medical assistance to minimize the loss of brain tissue. This device must accurately and frequently monitor signs of stroke with minimal obstruction to the user’s lifestyle, and it must do so in a less expensive manner than current hospital procedures to facilitate the desire to use the device.
Our solution is an iOS application that reduces overall duration for detection of stroke. Devices available today are focused on the treatment of stroke victims. The application will offer diagnostic abilities unavailable with current devices.
The results include 99% accuracy for the user interface and 97% accuracy for stroke tests. The degree of the stroke will be calculated based upon partnership with neurologists as well as the NIH stroke scale. This categorizes the severity of a present stroke on a scale of 0-4 with 4 requiring immediate care. The testing of the application will be executed using practicing physicians who will model typical actions of a potential client.
EEG Monitoring for Drowsiness Detection while Driving
Michael Drakopoulos, Ruchi Patel, Osazuwa Osarenkhoe, Jarrod Wagner
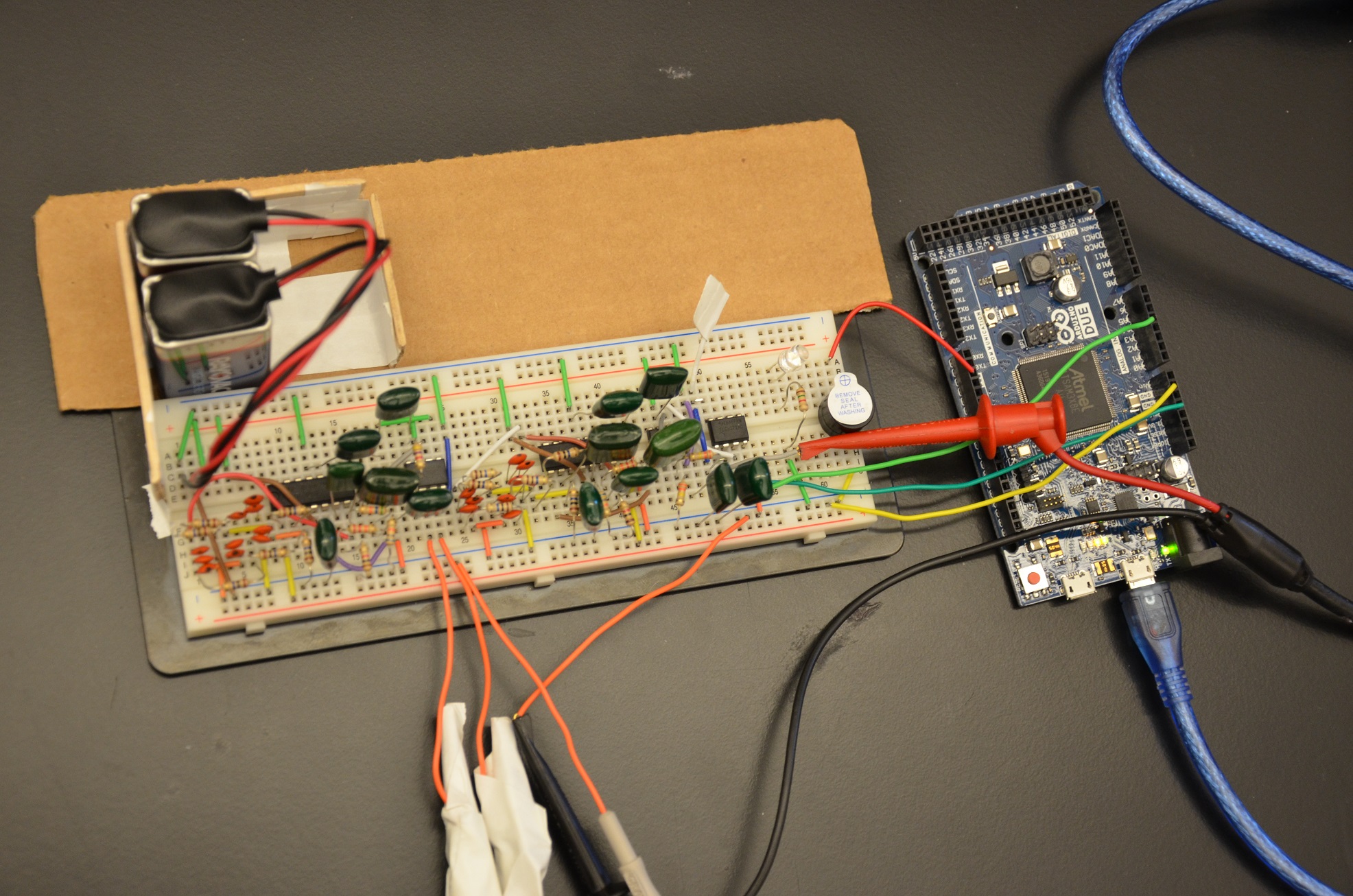
Driving while drowsy significantly impairs a driver’s reaction time, presenting a serious threat to the safety of the driver, passengers, and others on the roadway. Each year in the United States, drowsy driving directly contributes to seven percent of all crashes, or approximately 100,000 accidents, and results in 1,550 deaths, 71,000 injuries, and $12.5 billion in damages. Currently implemented methods of detecting driver drowsiness focus on monitoring driver’s drowsiness with indirect physiological signals. On the other hand, changes in the mental state of the driver are a more direct indicator of alterations to his/her characteristic pattern of interaction with the vehicle. Thus, detecting drowsiness while driving is very crucial to avoid accidents; there is a need for a direct method of measuring drowsiness to reduce detection time and subsequent feedback. We have developed a method of using electroencephalography, or EEG, to directly record changes in brain activity correlating to drowsiness as part of a system to provide feedback to drivers to alert them of their mental state. The ability of EEG to detect sleepiness in real time during driving has been well-documented in previous research, and some systems providing drowsiness-based feedback have been developed. However, these alternative solutions face numerous limitations, including problems with legality in multiple states for covering the ears of the driver when in use, device being bulky and expensive when applied as part of wireless systems. Our solution improves upon these alternatives by utilizing a legal, low-cost design. It is innovative in its unique synergistic combination of time and frequency measurements to determine when a driver is drowsy. Our results have demonstrated our ability to acquire the desired EEG signals, and distinguish between drowsy and alert states through the use of EEG signals and provide feedback to a user on his/her state of drowsiness.
Portable Biosensor
Jonathan Hsu, Axel Masquelin, Ryan Preston, Andrew Witten
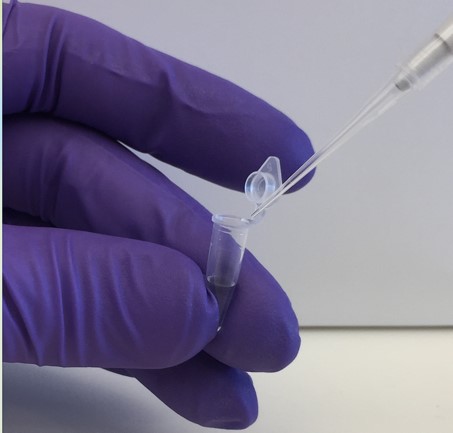
In 2015, the World Health Organization estimated that there were over 2 million cholera cases worldwide. After the 2010 earthquake in Haiti, a cholera epidemic spread throughout the nation, infecting over 200,000 people within six months. Cholera still devastates the population today. Vibrio cholerae (V. cholerae) is a water- and foodborne pathogen which causes diarrhea, vomiting, and dehydration in patients, and, if left untreated, ultimately leads to death. Rapid detection of V. cholerae in drinking water sources prevents such outbreaks. Currently, rapid diagnostic tests that perform field assays do not exist for cholera testing in water samples. This is due to the low environmental concentration of V. cholerae present in water (as few as 10 cells/mL). There is a global need for a device to detect V. cholerae in drinking water sources at these low concentrations that is accurate, portable, cost effective, and with a 95% sensitivity and specificity. To respond to this need, we propose a portable smartphone attachment and application within a kit that detects the presence of V. cholerae. Using the biological assay technique known as loop mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), V. cholerae DNA from an environmental water sample can be amplified and measured quantitatively using our smartphone application. Our solution addresses the design criteria for a rapid field assay capable of working at low concentrations (10 cells/mL) in less than 20 minutes and has a sensitivity and specificity higher than 95%.
Saving the Rhino: One Ultrasound at a Time
Karlie Daff, Laura Jamicich, Alexa Nelson, Ryan Steinke
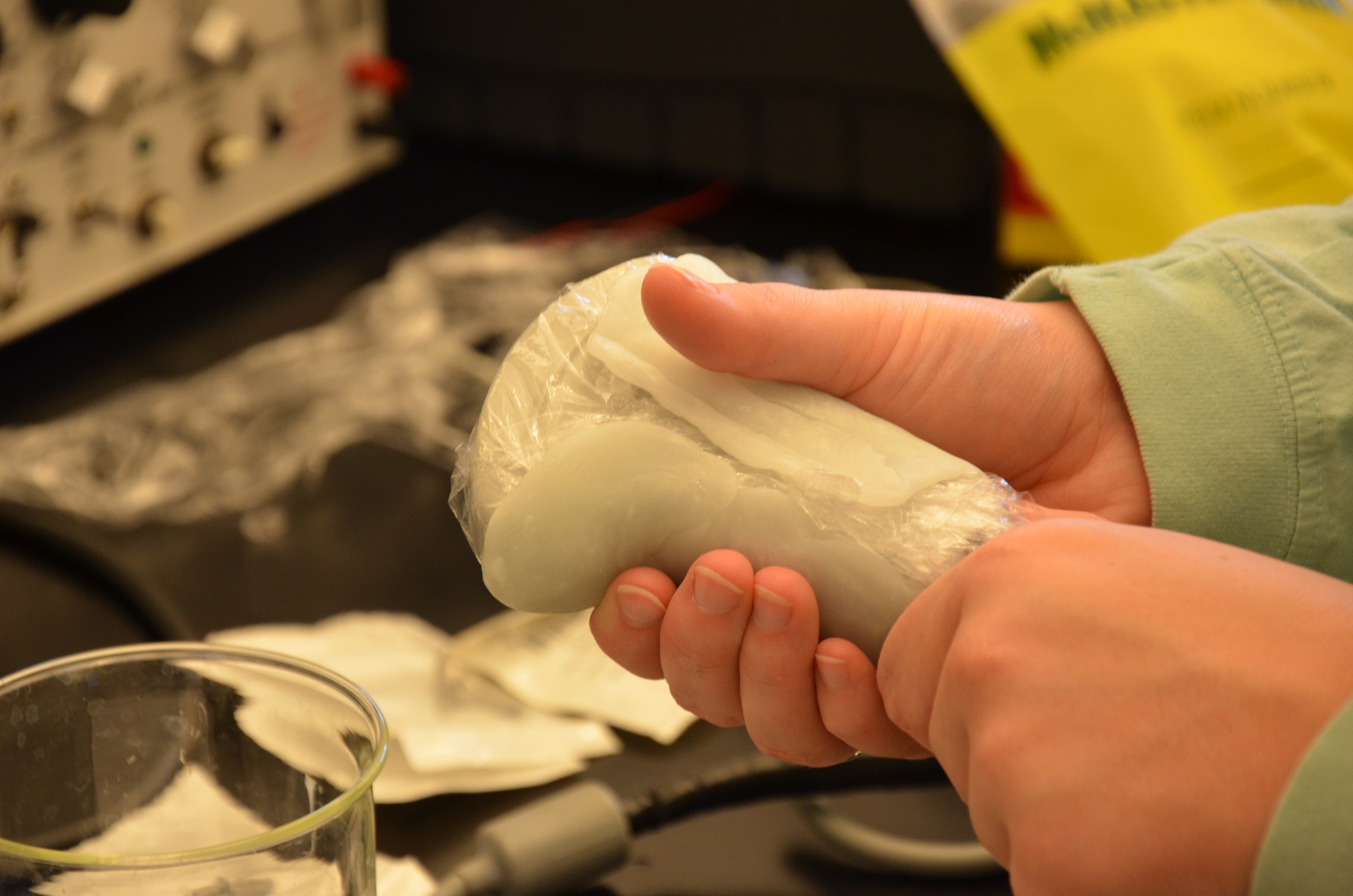

Rhinoceros play an important role in the tourism industry in Africa, but they are at risk of extinction within the next three generations. Therefore, conservation efforts take place in zoos and wildlife refuges to help monitor female reproductive health in order to improve the success of artificial insemination efforts. Ultrasound is current method being used to assess the reproductive abilities of the female rhinoceros. Due to thick skin and limited penetration depth of current ultrasound systems, they must be performed trans-rectally. A partnership has been formed with the Indianapolis Zoo, where there is a desire to use a new ultrasound transducer that will produce a higher quality image, allowing the veterinarian to better monitor the female’s reproductive health. The new transducer does not fit the current extension device, therefore, there is a need for a newly designed probe extension device. The designed probe extension accommodates the new transducer shape, has the ability to change transducer angles, has new length and weight advantages, and is user friendly. The device design is one that modeled the design of an inspection mirror. It has a handle that the user squeezes in order to adjust the angle of a hinge attached to the transducer. The transducer is placed in custom molded fixture and the entire device is house in a plastic housing unit. The device is able to reach a full 90° rotation, it can be sterilized with bleach and ammonia, and is water resistant, meeting all major customer needs. As large animal ultrasound probe extension devices are not a commercialized product, the design is one that is unique to the needs of the Indianapolis Zoo and one that cannot be found elsewhere on the market.
ProGraft: The Proactive Solution to a Long-Lasting Hemodialysis Graft
Rebecca Foley, Moriah Garcia, Trace Maurer, Daniel Shyu
_cp.jpg) Nearly 500,000 Americans currently suffer from end stage renal disease and require dialysis to supplement or replace their kidney functionality. Currently, 19% of dialysis users have an implanted arteriovenous graft to transfer blood from the body. However, annual maintenance costs for grafts are about $5,000 per patient due a high two-year failure rate of 70%, creating nearly a $3 billion industry. These high failure rates are due to stenosis and clot formation that prevent the necessary blood flow, as well as trauma from repeated needle puncturing for each treatment. As a result, there is a clear need to update the current design to extend the lifespan of dialysis grafts by removing cell growth from the walls and preventing the tearing of the graft material. The proposed solution will physically remove the buildup of cells along the wall inside the graft design and prevent any substantial accumulation over time. Preliminary results show cell removal based on previous studies. Furthermore, the device has successfully withstood 650 treatments, which simulates the number of punctures over three years. Given its substantial improvement from existing vascular access methods in dialysis, this device should lead to an increased number of patients utilizing grafts. This novel design addresses the major existing issues with arteriovenous grafts, eliminates the need for additional procedures, and improves both longevity and effectiveness for patients requiring hemodialysis.
Nearly 500,000 Americans currently suffer from end stage renal disease and require dialysis to supplement or replace their kidney functionality. Currently, 19% of dialysis users have an implanted arteriovenous graft to transfer blood from the body. However, annual maintenance costs for grafts are about $5,000 per patient due a high two-year failure rate of 70%, creating nearly a $3 billion industry. These high failure rates are due to stenosis and clot formation that prevent the necessary blood flow, as well as trauma from repeated needle puncturing for each treatment. As a result, there is a clear need to update the current design to extend the lifespan of dialysis grafts by removing cell growth from the walls and preventing the tearing of the graft material. The proposed solution will physically remove the buildup of cells along the wall inside the graft design and prevent any substantial accumulation over time. Preliminary results show cell removal based on previous studies. Furthermore, the device has successfully withstood 650 treatments, which simulates the number of punctures over three years. Given its substantial improvement from existing vascular access methods in dialysis, this device should lead to an increased number of patients utilizing grafts. This novel design addresses the major existing issues with arteriovenous grafts, eliminates the need for additional procedures, and improves both longevity and effectiveness for patients requiring hemodialysis.
Low-Cost Accessible CPR
Shadman Jubaer, Michael Dziekan, Vicki Sell, Sudhanshu Manda
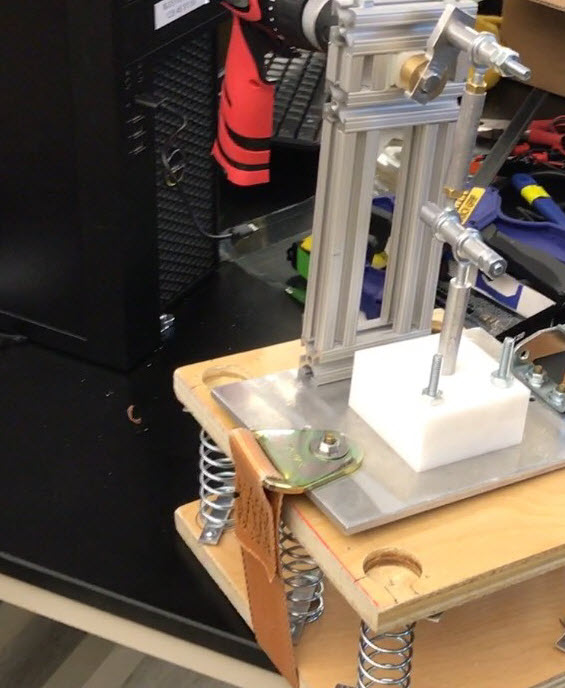 Approximately 90 percent of patients who suffer out-of-hospital cardiac arrest die. Often rescuer fatigue after more than 2 minutes of continuous CPR makes it almost impossible to deliver effective resuscitation. In rural areas this problem is compounded by the lack of access to trained professionals, and the long delay to receive adequate medical care. After the magnitude 7.8 earthquake in Ecuador on April 2016, first responders were unable to deliver CPR to hundreds of victims, resulting in preventable deaths. Though automated CPR devices such as the AutoPulse, ROSC-U, and LUCAS-2 exist, the prohibitive cost of such devices (minimum $12,000) make them inaccessible for the average patient in Ecuador.
Approximately 90 percent of patients who suffer out-of-hospital cardiac arrest die. Often rescuer fatigue after more than 2 minutes of continuous CPR makes it almost impossible to deliver effective resuscitation. In rural areas this problem is compounded by the lack of access to trained professionals, and the long delay to receive adequate medical care. After the magnitude 7.8 earthquake in Ecuador on April 2016, first responders were unable to deliver CPR to hundreds of victims, resulting in preventable deaths. Though automated CPR devices such as the AutoPulse, ROSC-U, and LUCAS-2 exist, the prohibitive cost of such devices (minimum $12,000) make them inaccessible for the average patient in Ecuador.
There is a dire need for a low-cost, portable, automated CPR device to combat lack of access, rescuer fatigue, and to keep patients alive in rural areas long enough to receive advanced medical care. To address this need, the team is proposing a portable automated CPR-device that costs less than $1000 to manufacture and distribute. The device will be easy to use, and can be operable with minimal training and education.
This project is currently within the prototyping process. Preliminary tests on electromechanical components have shown the device can deliver the necessary compression while unloaded. The device will be tested for environmental durability after full system integration is complete.
PosturePack
Bridget Perry, Matt Churik, Scott Irving
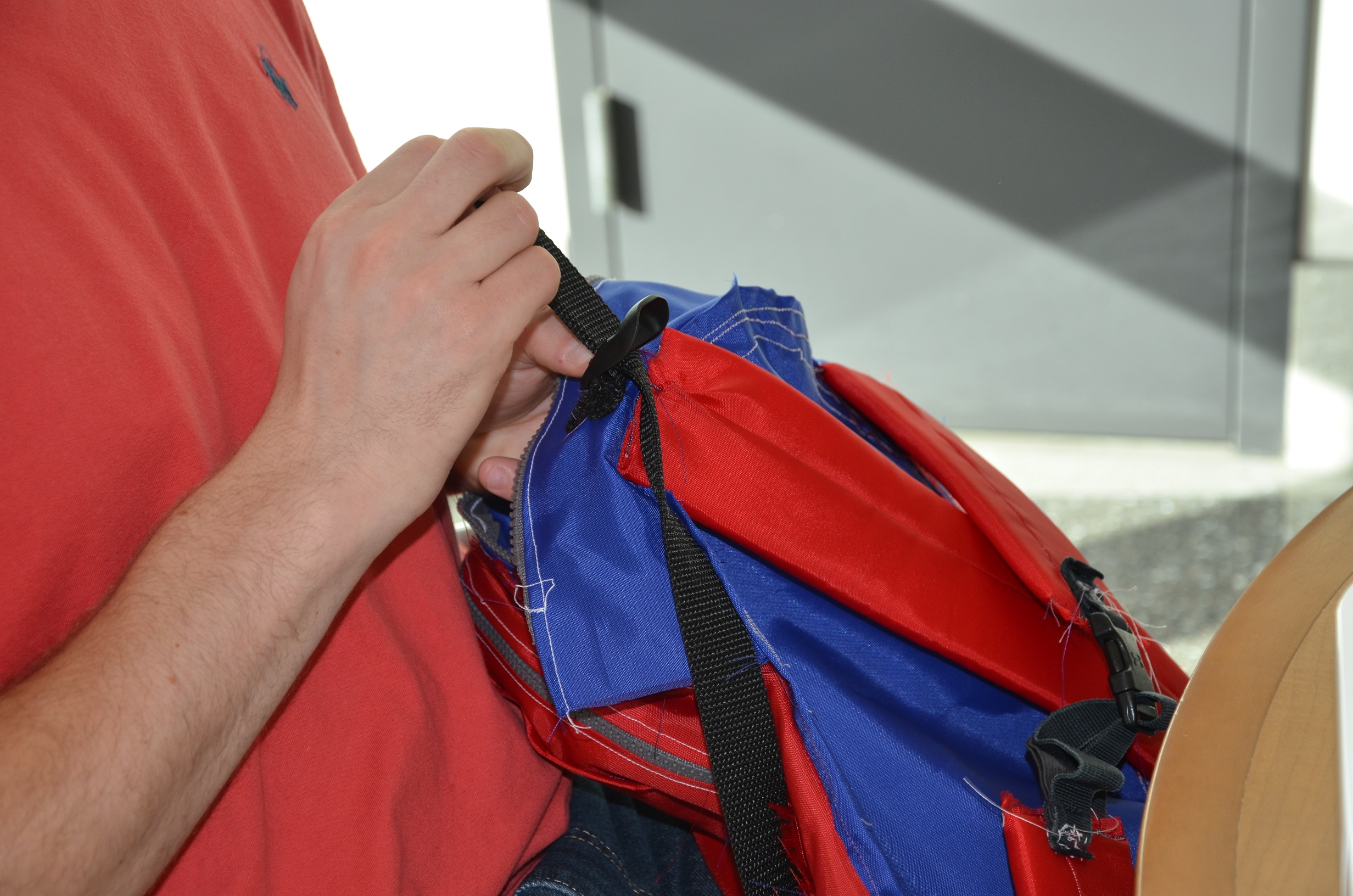

According to the American Academy Orthopedic Surgeons, children who carry loads greater than 10-15% of their body weight are at risk to develop lifelong problems resulting from poor posture. Heavy loads carried via backpack lead to a forward head posture, resulting in neck pain, vertebral bodies’ disorders, compressed disks, and lower back pain.
A method is needed to address the development of poor posture in children due to heavy loads and ineffective load displacement of backpacks. The solution needs to maintain proper posture when heavy loads are carried, demonstrated by a craniovertebral angle (CVA) between 60° and 65° and a trunk forward lean (TFL) between -2.5° and 2.5°, while maintaining a suitable level of pain.
Our design solution is a posture improving backpack that includes a cross shoulder strap system, a lower back adjustable support insert, and a pulley system. The cross shoulder straps maintain proper shoulder placement by preventing them to roll forward. The lower back support insert assists in maintaining a proper lumbar spine curvature of 20-40 degrees. Finally, the pulley system redistributes the weight of the backpack on top of the shoulders, reducing the moment on the body.
The PosturePack prevents poor posture development by redistributing the weight of the load vertically over the user’s center of gravity. Effectively, this would decrease the moment of the load and reduce the need for the user to lean forward. There was a statistically significant difference between the PosturePack and normal backpacks in average CVA and TFL for expected loads. Poor posture starting at an early age due to heavy loads can have long lasting effects leading to future back and neck problems. The PosturePack aims to reduce these risks for a healthier future.
Balancing Assistive Device for Peripheral Neuropathy
Nicholas DiCola, Agnes Doszpoly, Evan Markley, Adrianna Payne
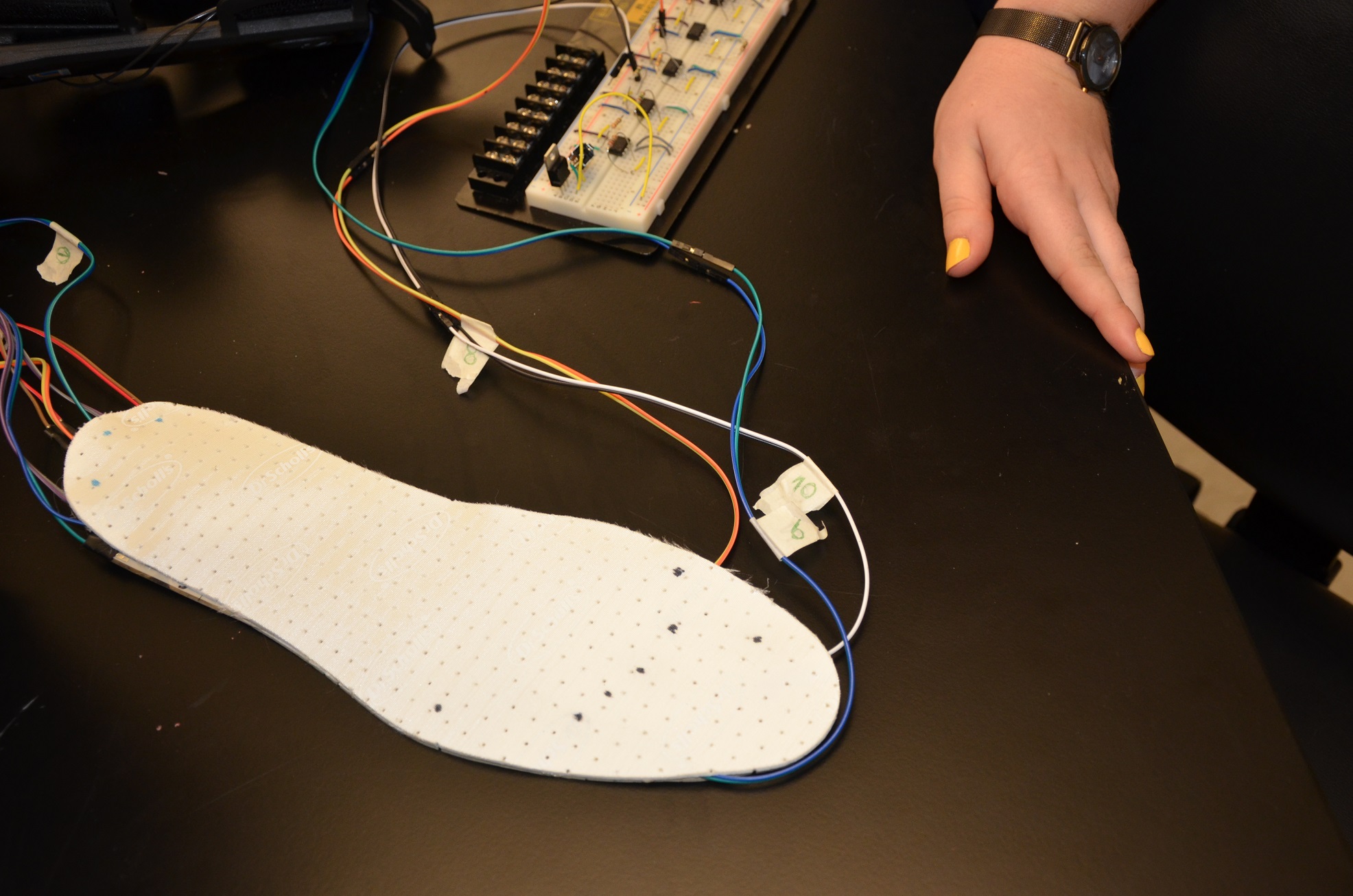
Peripheral neuropathy (PN) is defined as neuron death of the periphery, particularly the hands and feet. This condition currently affects an estimated 20 million people in the United States. Diabetics are prone to develop irreversible sensory PN, but with maintained motor function. Because of the role of tactile sensation in balance, these individuals are highly susceptible to falling. There is a need for an assistive device that will allow patients with irreversible sensory PN, but working motor function, to sense weight distribution through means other than their feet. The solution, "Sway No More", is an assistive device that remaps the balance reflex of the leg through repeated coupling of stimulation and motor reaction. Over time and with training, the motor neurons originally linked to sensory neurons in the feet will become linked to those of the thigh (due to the naturally adaptive nervous system). The first component of our solution is a foot insole with ten imbedded pressure sensors. The second is an array of vibrational motors, enfolded in an elastic mesh, placed in the same spot on the skin of the anterior portion of the lower thigh with a modified knee brace. Currently, the foot insole is fully integrated with the thigh patch and can detect and stimulate a gradient of pressure applied to the foot insole and the thigh patch. Validation testing will begin in the coming weeks. The solution is an in-the-shoe foot insole that detects the pressure distribution and stimulates vibrational motors held in place by a modified knee brace which re-map the sensory nerves of the foot to the thigh. The impact on the medical field would be an alternative to PN patients for improving daily functionality.
3-D Vein Mapping Using Active Trans-illumination and Impedance Sensing Devices for Assistance in Pediatric Venipuncture
Puneet Anantharam, Yumin Gao, Katherine Lin, Connor Turnipseed
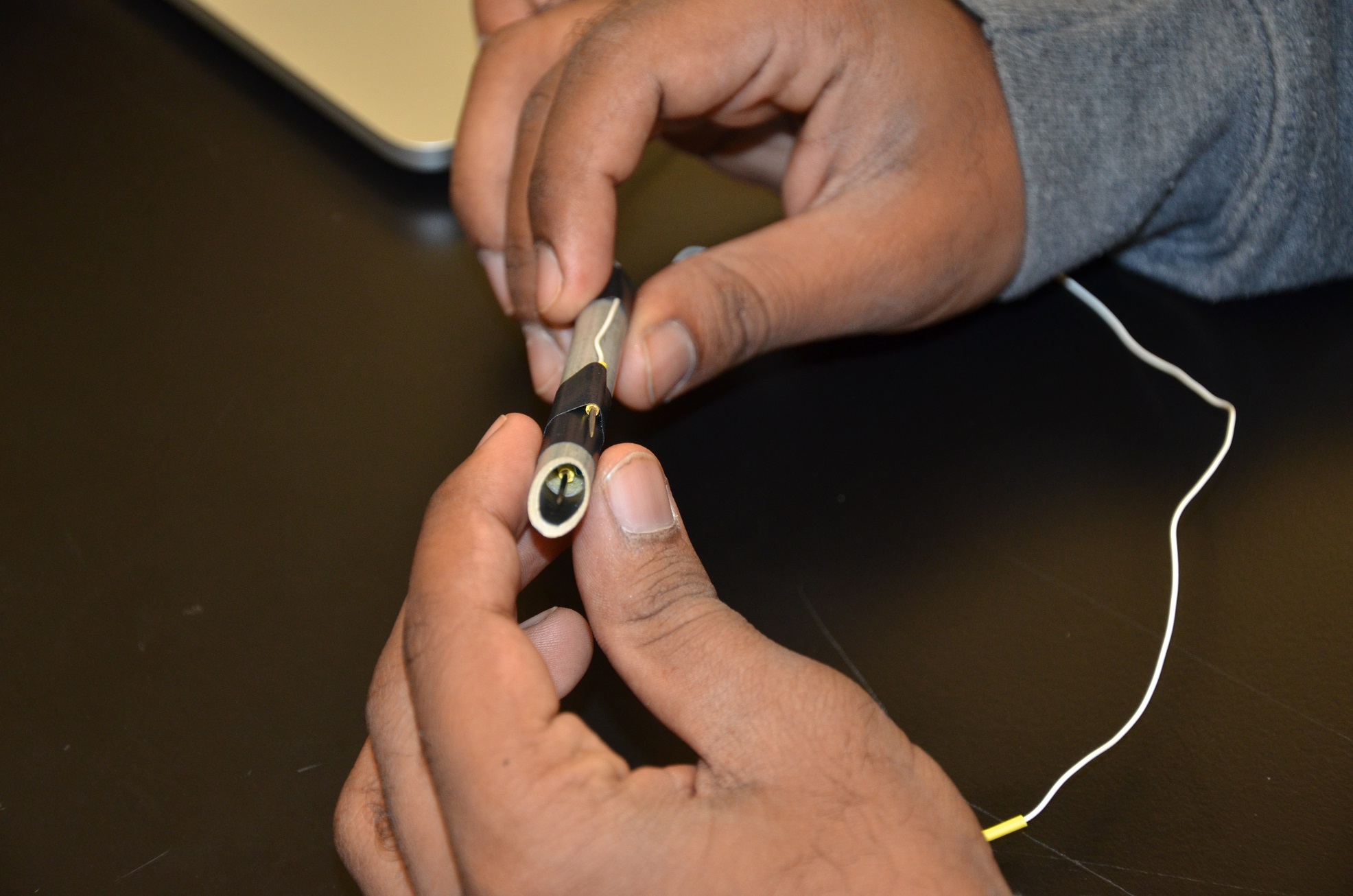
Intravenous (IV) administration in children (ages 1 – 21) is a common, challenging, and painful pediatric procedure. In a study on needle phobia, approximately 5 million children in the United States experienced high discomfort during a venipuncture procedure. Due to smaller sizes of peripheral veins and more tender surrounding tissues, erroneous administrations occur frequently. Another study covering 249 pediatric peripheral IV insertions showed that only 53% of insertions were successful on the first attempt. Therefore, there is a clinical need for a modality that establishes access to subcutaneous veins in children that provides effective detection of veins, ensures proper positioning of the needle within the vasculature, and reduces pain and distress experienced by the patient. The Guided Pediatric VeniPuncture Kit, composed of the VeniPatch and PiNeedle, serves to establish access to subcutaneous veins in pediatric patients. The VeniPatch facilitates two-dimensional and non-invasive vein scanning. The PiNeedle distinguishes venous vasculature from subcutaneous tissue based on characteristic impedance values. Together, the devices determine vein location and provide real-time feedback to practitioners. During testing, the devices demonstrated a 32% improvement in success rate and pain reduction by 1.42 units on the Wong-Baker FACES pain scale compared to the standardized procedure (t = 4.9785, p < .001 and F = 39.41, Partial h2 = 0.36, respectively).
The innovation of this technology lies within its focus on unmet pediatric needs, adaptability to current needle markets, and integration of various biomedical advancements. The pediatric global IV access market, including IV catheters, needles, and infusion pumps, is estimated to reach a value of 11.6 billion dollars by 2019. The accessibility of this device kit fulfills the needs of global pediatric patients and medical practitioners.
Smart Knee Sleeve
Sriram Boppana, Rohith Jayakumar, Daniel Haugan, Jacques Stites
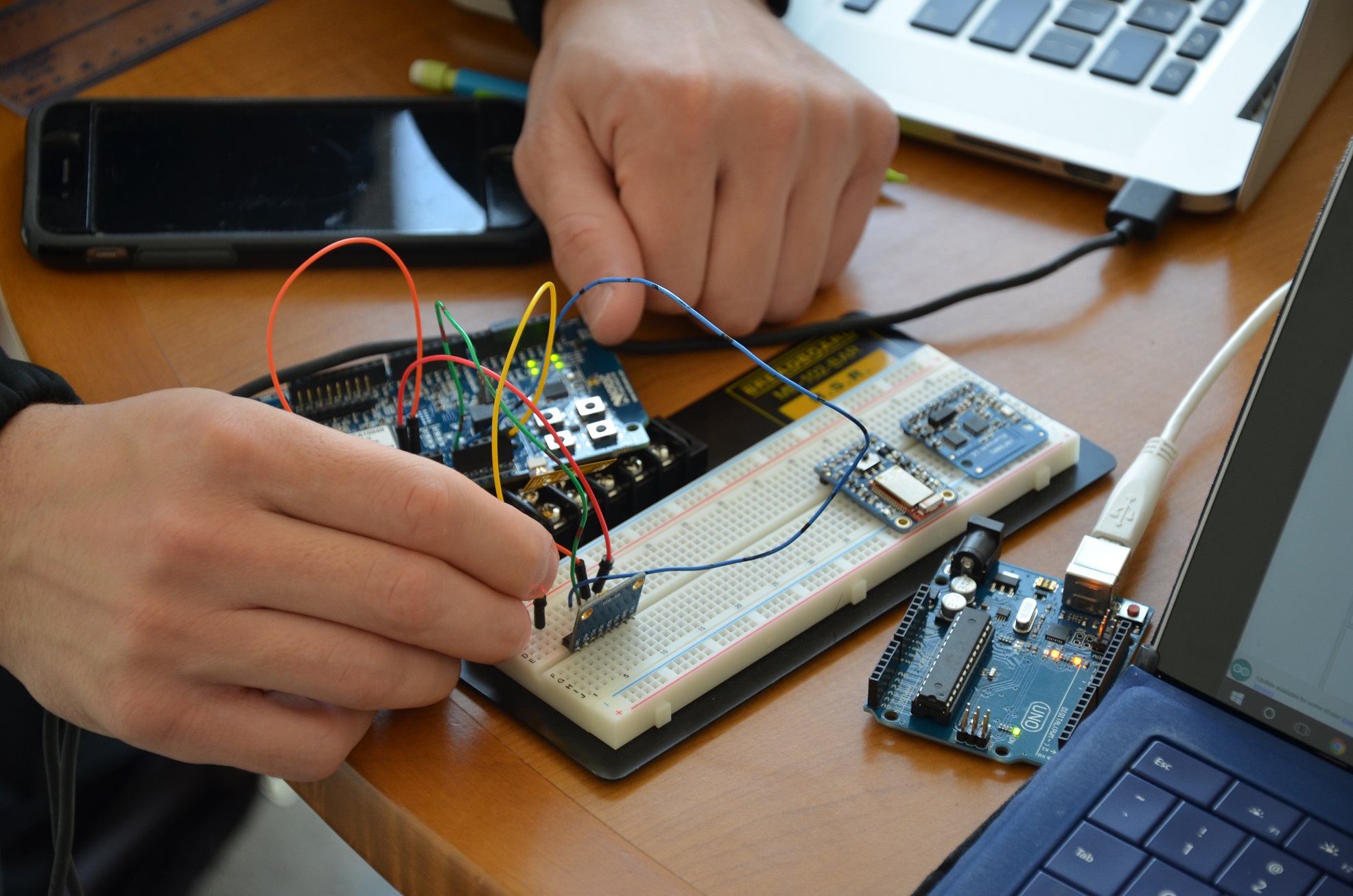
Amateur athletes and patients with musculoskeletal knee injuries do not have a method to consistently monitor and ensure that they are using proper form while exercising. Proper monitoring of the knee mechanics, such as flexion and extension, is essential for prevention of recurrent and costly injuries that may occur due to improper exercise form. There is currently no low-cost, simple, and individualized method of ensuring proper form over a wide variety of exercises for both injury prevention as well as injury rehabilitation. The market for this type of product is potentially large. ACL tears alone account for approximately 200,000 cases per year in the US.
Embedded system design applications provide an optimal way to quantitatively monitor knee and leg angles, ensure proper exercise form in a low-cost, and not impede mobility. In order to accomplish this, a microprocessor, two microelectromechanical system (MEMS) accelerometers, a custom printed circuit board, and a phone application are integrated together to effectively collect data and communicate recommendations to the user. After initial prototype testing, knee angle measurements obtained from the preliminary prototype indicate consistent and accurate measurements for an extensive number of flexion and extension cycles on the knee. This device has also been proven to be nonrestrictive and yet durable enough for nearly any land based activity through rigorous water resistant, impact resistant, and user movement testing.
Ultimately, this device allows both athlete and knee injury rehabilitation patients to monitor their activity and ensure proper form over a wide variety of exercises. A modified knee sleeve is unique because it integrates innovative exercise technology in a sleeve that is comfortable for athletes to wear.
Keeping an Eye On Contact Lenses
Agni Dhanabal, Manji Fu, Amanda Schneeweis, Gang Seo
Contact lenses sit atop the cornea to correct vision. Direct contact can result in the development of micro-abrasions on the cornea, leaving the eye more susceptible to infection upon exposure to infectious agents. Bacteria – more specifically Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus – have been known to proliferate on contact lenses and on the cornea, and can cause eye infections such as keratitis. Each year, approximately 1 million doctor visits occur as a result of keratitis, costing an estimated $175 million and 250,000 clinical hours. According to the Center for Disease Control, 60%-70% of such eye infections are the result of improper maintenance or usage of contact lenses. It is reported that 40%-90% of contact lens users fail to clean their lenses properly, leading to bacterial proliferation, and ultimately eye infections. As such, the incidence of bacterial eye infections can be significantly reduced by proper care of contact lenses. This can be achieved by redirecting the responsibility for the cleanliness of the lenses from the user to a more reliable autonomous process. The solution to this problem will be a device that uses a magnetic stirring bar in conjunction with UV radiation to destroy any bacteria on the contact lens as well as wash off lipid, protein, and biofilm build-up. The results of 254nm UV light on both bacterial strains show that 20s of exposure destroys 99.99% of bacterial spores on an agar plate. The effectiveness of the stir bar in detaching bacteria from the lenses is still being evaluated, with comparison to sonication as a control. By combining the germicidal effect of the UV light and the induced turbulence in an automated process, the solution will present a novel and dependable method for users to clean and disinfect an everyday necessity while saving time and effort.
Medication Reminder Device
Benjamin Chun, Sydney Gorman, Shan Lu
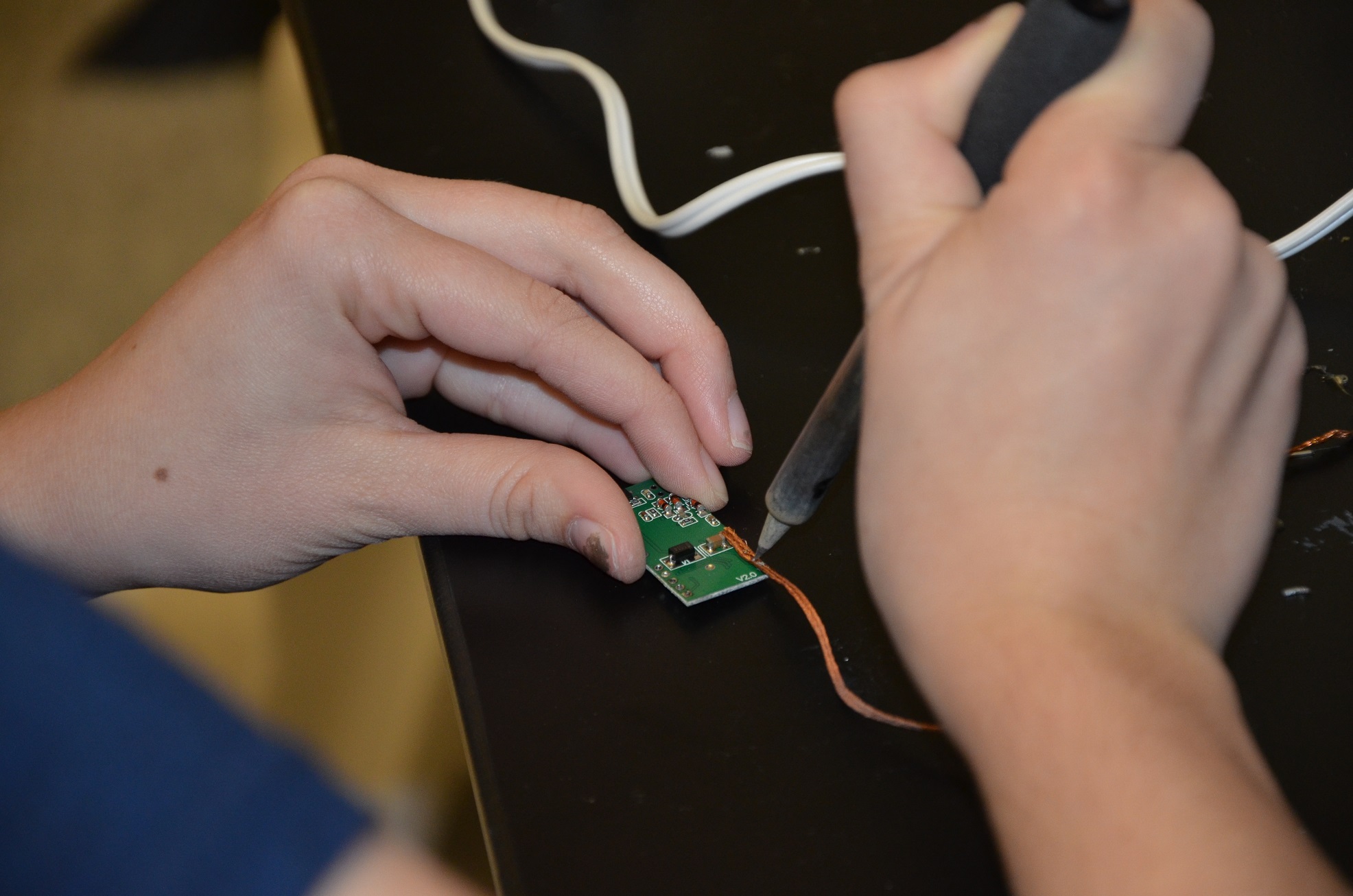
Current study shows that depressed patients are three times more likely than healthy individuals not to adhere to their medication. When a depressed individual misses their medication, their quality of life can decrease and they may experience a relapse in their depression that can lead to self-harm or even suicide. The main reported reason for non-adherence to antidepressants is simply forgetting to take them. There is a need for a system that can increase medication adherence and displays positive results to patients. Our proposed solution is a wearable device that serves as a physical reminder integrated with a smartphone application to track patients’ adherence as it improves. The wristband reminds the user when medication must be taken and either times out or is disabled by touching the pill bottle tag to the wristband. The smartphone application consists of a page for personalized settings for the wristband such as time and alarm patterns, a questionnaire to determine the mood of the user, a graphical representation to display these moods over time, and information related to the type of medication they are taking and contact for their doctor if they are constantly missing their medication. The wristband and smartphone application will together increase the medication adherence in depressed patients and encourage them to take their medication on time by showing the positive impact it has for them.
PneuDia: A Portable Pneumonia Sensor Employable in Low Resource Areas
Asif Ashraful, Gregory Berglund, Quefei Chen, Curtis Slaubaugh
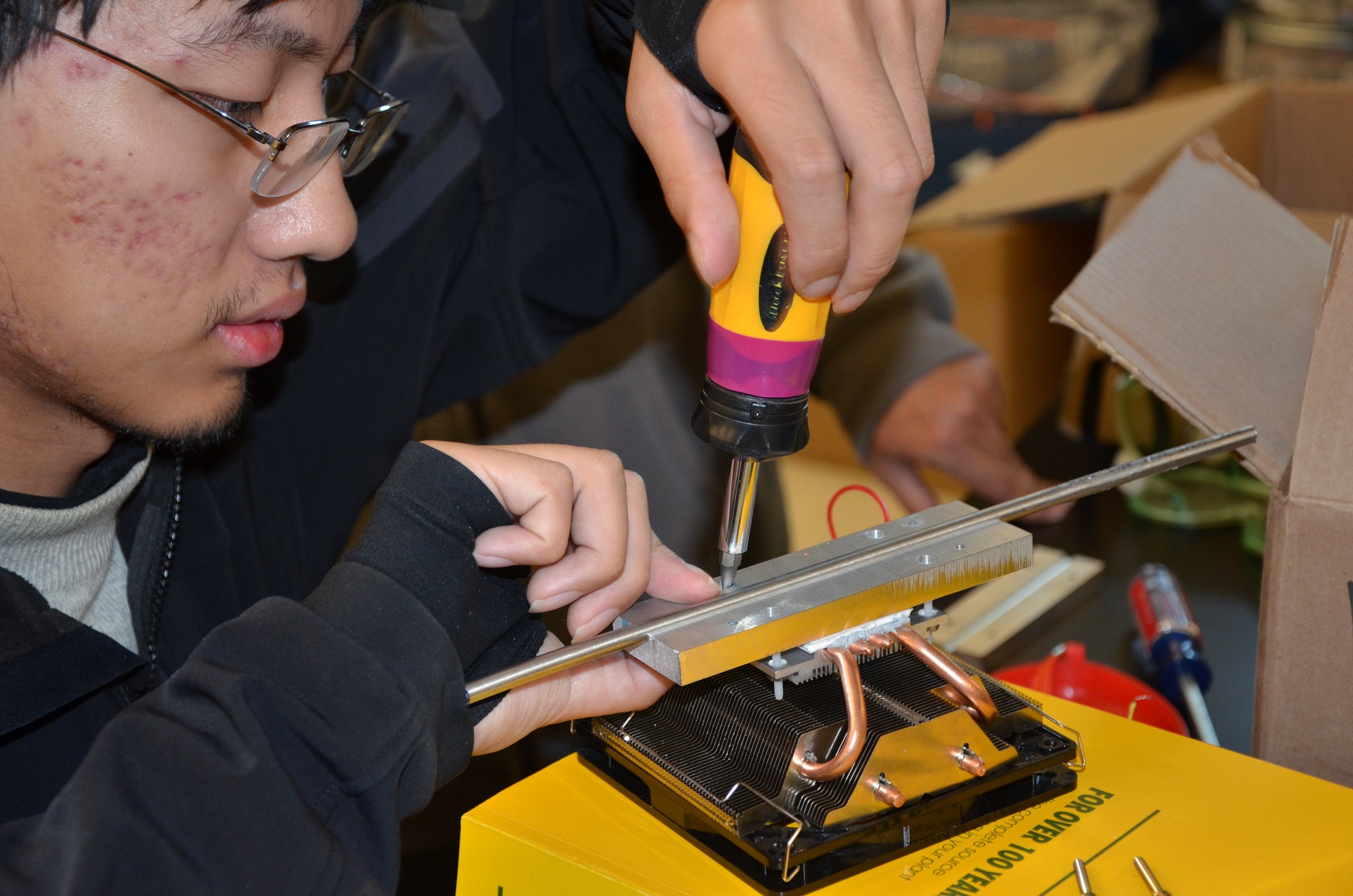

Currently, over one million children worldwide die each year due to complications from childhood pneumonia. Many of the potentially preventable cases go unnoticed due to the inability of high prevalence areas to use expensive equipment or gain the required expertise to perform chest X-rays or blood cultures. There is a need for a low-resource diagnostic device to detect cases of childhood pneumonia. The developed design solution obtains a patient sample from the lungs. This sample is then transferred to tubes prefilled with reagents necessary to carry out a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay. The tubes are housed in a joint incubating and viewing box that will illuminate the samples using blue light emitting diodes, which will allow positive samples to fluoresce in the presence of targeted pathogens and negative samples to remain dull. Results have indicated the ability to successfully detect amplification via fluorescence within 30 minutes for 90% of samples. Additionally, current methods are unable to distinguish between viral, bacterial, and fungal causes of pneumonia. By using three separate tubes, with primers uniquely designed to target common viral, bacterial, and fungal causes in different tubes, the device will be able to provide an indication to the clinical worker of what form of pathogen has infected the patient. This information is valuable in the fight against antibiotic resistance, as the most common form of diagnosis in low resource areas remains clinical observation, commonly leading to the prescription of unnecessary antibiotics.
C-EAR – Canine Equipment for Acoustic Research
Claire Albertz, Joseph Muskat, Alexander Ocken, Katherine Powell
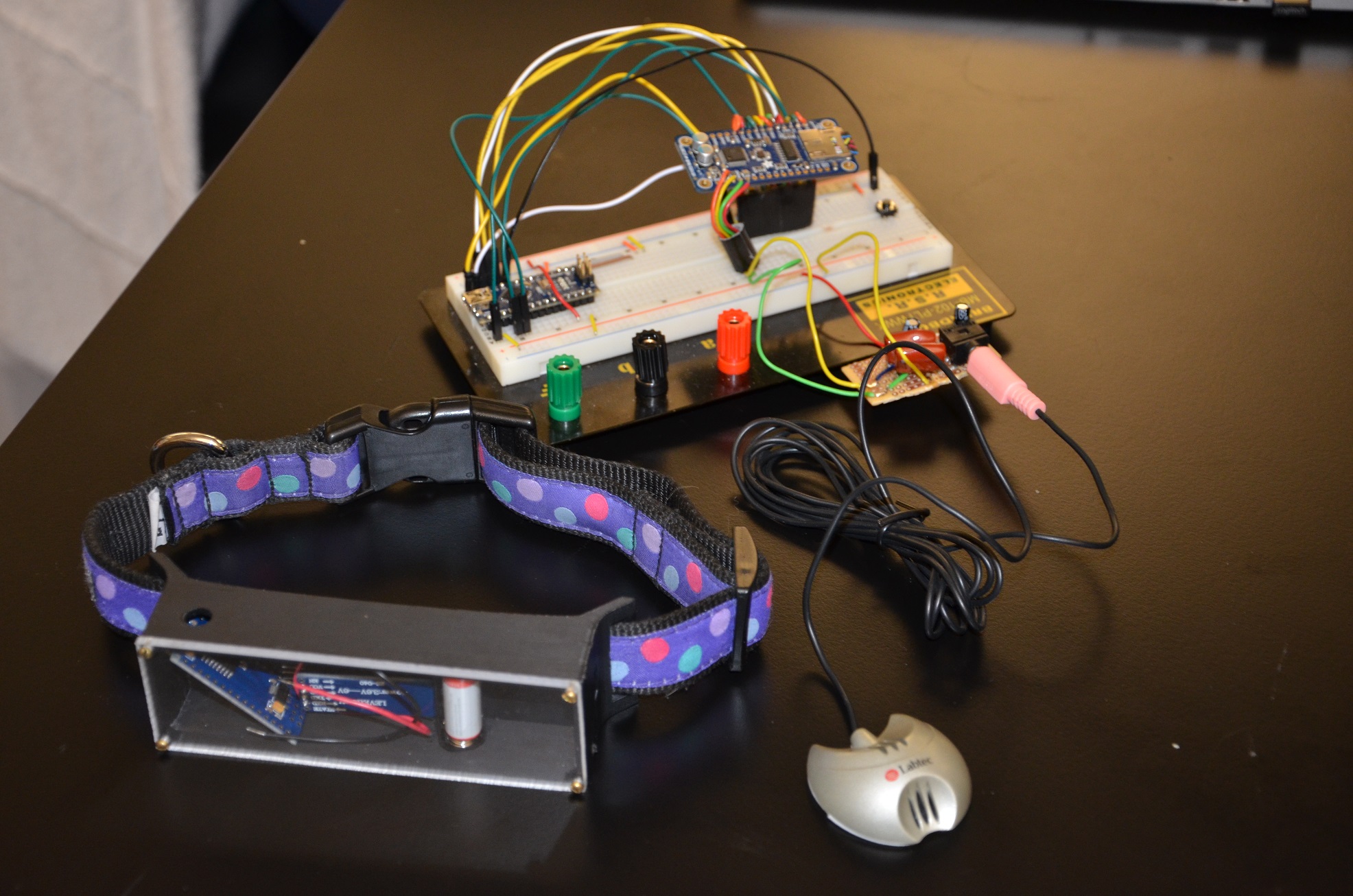
More than 800,000 people receive medical care due to dog bites in the United States each year - costing $483 million in 2013. Strikingly, most common incidents involve a child and a familiar dog. In order to monitor canine aggression and alert owners to emotional state, vocalization can be used to predict canine mentality. This study designs an ergonomic collar attachment to transmit vocalization data from canines to a computer. Concomitantly, pattern recognition software provides owners and researchers with a correlated emotional state. Skilled veterinarians use qualitative posture and vocalization observations to gage emotional state, but no device currently exists for objective vocalization analysis. There is a need to develop a tool for researchers and dog owners to monitor canine emotional states through vocalization correlation.
Customizable software for researchers enables dynamic trend monitoring. While the literature shows modern subjective identification of emotional state to fall between 20-58% accuracy, our results yield nearly 75% for the current testing configuration. Specifically, this device enables researchers to capture a top layer social activity that was previously qualitative and subjective.
For a commercial product design, a user interface will allow owners to record vocalizations from multiple dogs and display the predicted mood. The application will keep a history of the incidents, helping determine indicators and reasons for mood changes. This user friendly interface enables owners to monitor changes in behavior, identify potential health issues, and provide better information to help them care for their pets.
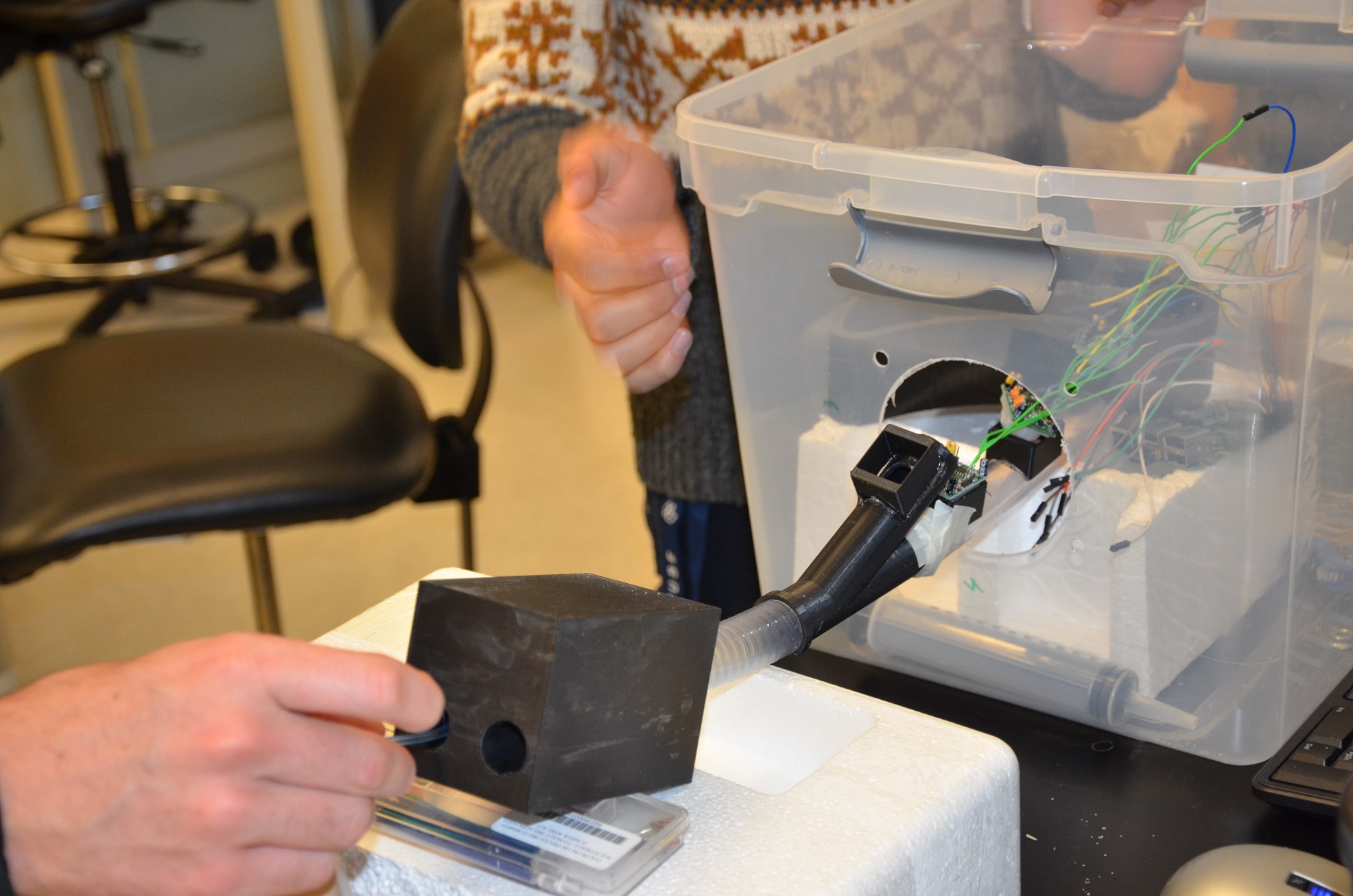
NID – Nasogastric Intubation Dummy
Cameron Locker, Fenil Patel, Konrad Wolfmeyer

Nasogastric tubes is a widely used convenient method to aspirate and administer stomach content and drugs to patients with many different complications. Current training methods cost more than thousand dollars and do not provide the user with adequate feedback for measuring success or failure. Hence, there is huge demand for solutions that are cheap and provide real time feedback. The solution devised by our team is unique because it provides real time feedback to the user by using passive infra-red sensors paired with a graphical user interface (GUI). There are four different subcomponents: the fluids system, the physical model, the electrical circuit and the GUI. The fluid system would deal with the artificial esophagus, trachea and stomach. The physical model would encompass everything related to the model such as the mannequin design and the nasal cavity. The electrical circuit and the GUI would be the front end of the system and the user would be able to control all the components through the GUI. Individual subcomponents were tested on their ability to perform their specific functions and later tested as a whole in the system. During testing, the sensors revealed one false positive for every six correct signals that was recorded. The solution would be tested with the assistance of five different health professionals, at three different times on three different occasions. The whole system test would assess the performance of the system and its ability to reduce the number of false positive results and provide accurate feedback. The whole project was completed within a budget of thirty six dollars.
