Millions with swallowing problems could be helped through new wearable device
Georgia A. Malandraki, an associate professor of speech, language, and hearing sciences in Purdue University’s College of Health and Human Sciences, and Chi Hwan Lee, an assistant professor of biomedical engineering and mechanical engineering in Purdue’s College of Engineering, founded Curasis LLC and serve as an acting chief executive officer and chief technology officer, respectively. They started the company to commercialize their wearable technology and move it as quickly as possible to clinics and people with swallowing difficulties.
A video about the technology is available at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IPY-ytpkGck. The technology is presented in the Dec. 13 edition of Science Advances.
“We want to provide a reliable, patient-friendly and affordable way to treat the millions of people with swallowing disorders,” Malandraki said. “Many devices to help these people are expensive, not able to be taken home and not accessible in many rural areas.”
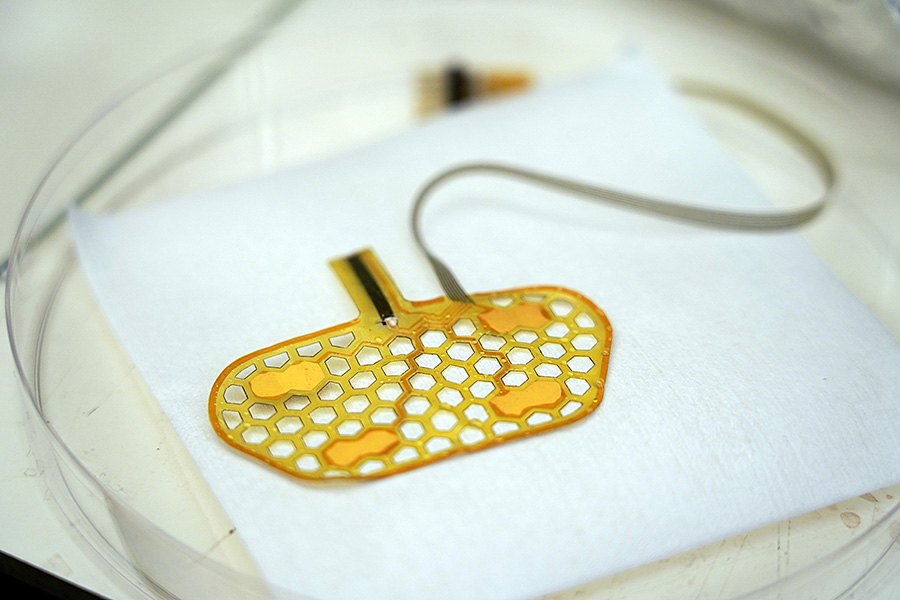
The researchers created a skin-mountable sensor sticker that attaches firmly to the neck area and is connected with small cables to a wireless transmitter unit.
The skin-mountable sensor sticker measures and records muscle activity and movement associated with swallowing. The information is then sent wirelessly by a separate unit clipped on the wearer’s shirt to software that stores it for later analysis by a doctor.
Successful completion of a swallow requires the precise coordination of more than 30 pairs of muscles of the head and neck, six pairs of cranial nerves, and complex circuitry in the brainstem and several brain areas. Any disruption in these pathways can result in severe swallowing disorders. More than 9 million adults and more than 500,000 children experience severe swallowing disorders each year in the U.S.
“Our device is unique in that we specifically created it to work well with the small and intricate muscles associated with swallowing events,” Lee said. “The sensor sticker is stretchable and flexible to work well with the skin and curvilinear head and neck shape, while the connected unit has electronic chips and more rigid components.”

The sensor stickers are disposable, designed with inexpensive components and meant to be used about 10 times before they are thrown away.
Malandraki and Lee have completed pre-clinical tests of the device and are currently conducting clinical trials. They are working with the Purdue Research Foundation Office of Technology Commercialization on patenting their technology. They are seeking additional partners. For more information, contact the Office of Technology Commercialization at otcip@prf.org and reference track code 2016-LEE-67542.
They also have worked closely with the Purdue Foundry, a commercialization hub in Purdue’s Burton D. Morgan Center for Entrepreneurship. Anne Smith, who retired as a distinguished professor in speech, language, and hearing sciences, serves as a senior advisor to the Curasis team.
Source: Millions with swallowing problems could be helped through new wearable device
Abstract
Flexible submental sensor patch with remote monitoring controls for management of oropharyngeal swallowing disorders
Min Ku Kim, Cagla Kantarcigil, Bongjoong Kim, Ratul Kumar Baruah, Shovan Maity, Yeonsoo Park, Kyunghun Kim, Seungjun Lee, Jaime Bauer Malandraki, Shitij Avlani, Anne Smith, Shreyas Sen, Muhammad A. Alam, Georgia Malandraki1 and Chi Hwan Lee
Successful rehabilitation of oropharyngeal swallowing disorders (e.g., oropharyngeal dysphagia) requires frequent performances of head/neck exercises that primarily rely on expensive biofeedback devices, often only available in large medical centers. This directly affects treatment compliance and outcomes, and highlights the need to develop a portable and inexpensive remote monitoring system for the rehabilitation and the tele-rehabilitation of dysphagia. Here, we present the development and preliminarily validation of a skin-mountable sensor patch that can fit on the curvilinear surface of the submental (under the chin) area in a non-invasive manner, and provide simultaneous remote monitoring of both muscle activity and laryngeal movements during swallowing tasks and maneuvers. This sensor patch incorporates an optimal design that allows for the accurate recording of submental muscle activity during swallowing and is characterized by ease-of-use, accessibility, reusability and cost-effectiveness. Preliminary studies on a patient with Parkinson’s disease and dysphagia, and on a healthy control subject, demonstrate the feasibility and preliminary effectiveness of this system.
