by _not_Exist_ | Jul 15, 2010 | 2010, HUMAN SHAPE INTERACTION, Karthik Ramani, Publications, Shape Understanding
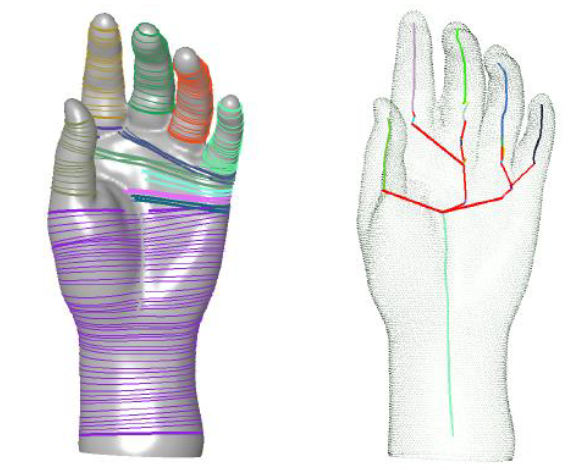
Abstract: Analysis of mesh models is gaining prominence as it has wide range of applications from engineering to medicine. In this paper, we present a method for analyzing meshes through the abstraction of its prominent cross-sections (PCS). An algorithm that can...
by _not_Exist_ | Dec 16, 2009 | 2009, HUMAN SHAPE INTERACTION, Karthik Ramani, Shape Understanding
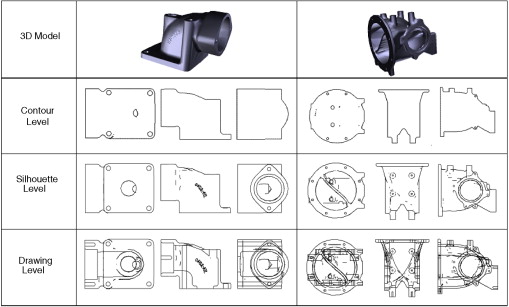
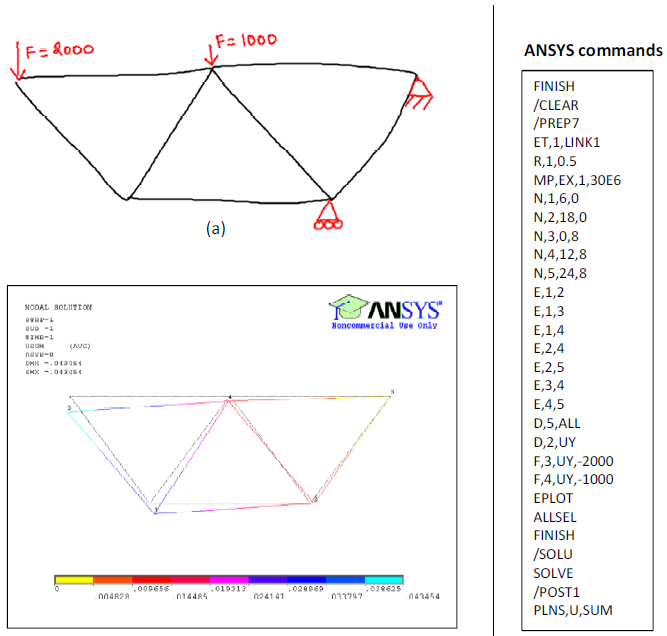
Abstract: 3D shape retrieval and clustering is of current interest in several different fields, including mechanical engineering. Several new shape representations for 3D objects are continuing to emerge. Most shape representations are embedded in a variety of feature...
by _not_Exist_ | Sep 16, 2009 | 2009, HUMAN SHAPE INTERACTION, Karthik Ramani, Shape Understanding
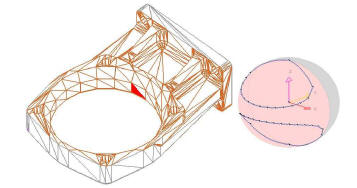
Abstract A global visibility map is a spherical image built to describe the complete set of global visible view directions for a surface. In this paper, we consider the computation of global visibility maps for regions on the boundary of a polyhedron. Both the...
by _not_Exist_ | Sep 16, 2009 | 2009, HUMAN SHAPE INTERACTION, Karthik Ramani, Shape Understanding
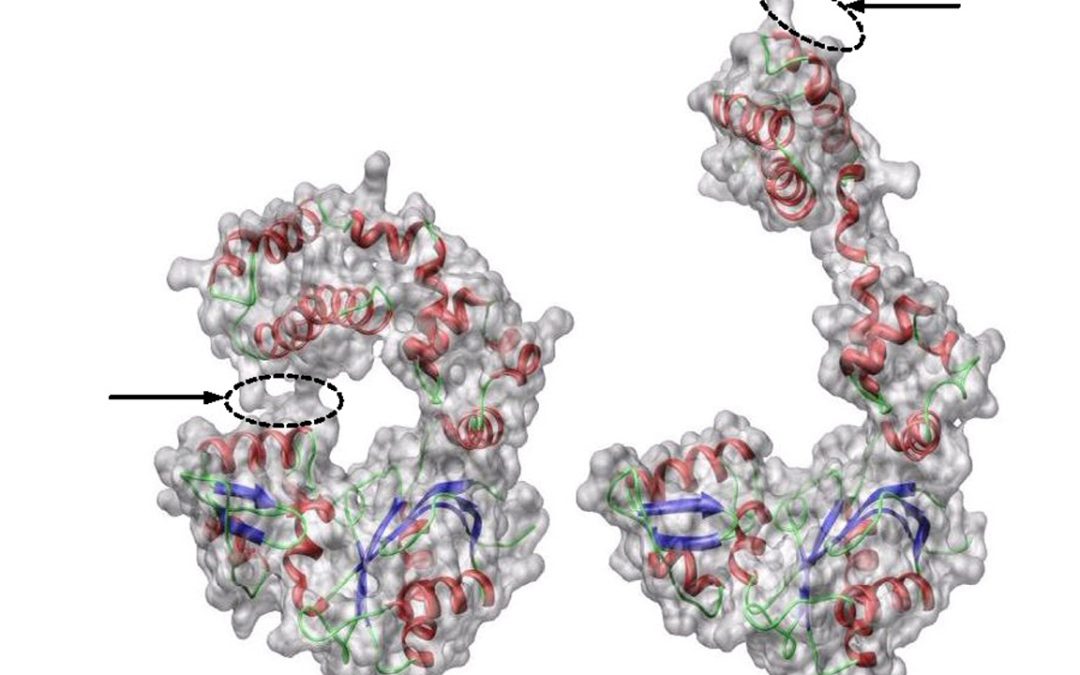
Abstract: Background: Techniques for inferring the functions of the protein by comparing their shape similarity have been receiving a lot of attention. Proteins are functional units and their shape flexibility occupies an essential role in various biological...
by _not_Exist_ | Sep 16, 2009 | 2009, Design Learn, DESIGN METHOD, HUMAN SHAPE INTERACTION, Karthik Ramani, Multi-touch Interaction
Abstract: The potential advantages of freehand sketches have been widely recognized and exploited in many fields especially in engineering design and analysis. This is mainly because the freehand sketches are an efficient and natural way for users...
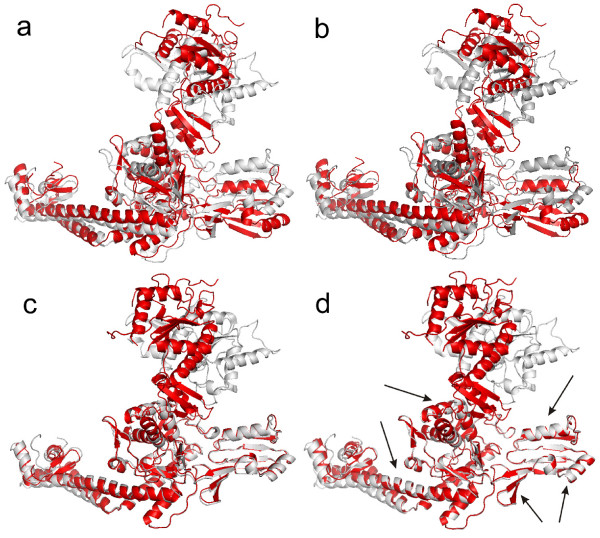
by _not_Exist_ | May 16, 2009 | 2009, HUMAN SHAPE INTERACTION, Karthik Ramani, Shape Understanding
Abstract: Background: The conventional superposition methods use an ordinary least squares (LS) fit for structural comparison of two different conformations of the same protein. The main problem of the LS fit that it is sensitive to outliers, i.e. large...