Context-aware AR instruction enables adaptive and in-situ learning experiences. However, hardware limitations and expertise requirements constrain the creation of such instructions. With recent developments in Generative Artificial Intelligence...
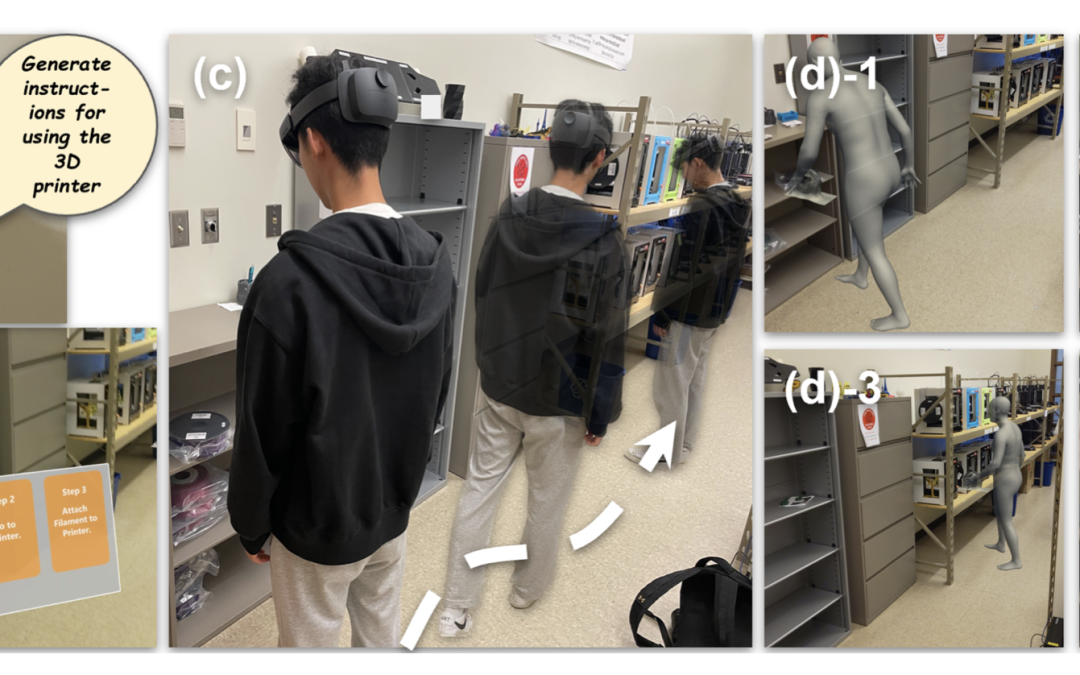


Context-aware AR instruction enables adaptive and in-situ learning experiences. However, hardware limitations and expertise requirements constrain the creation of such instructions. With recent developments in Generative Artificial Intelligence...
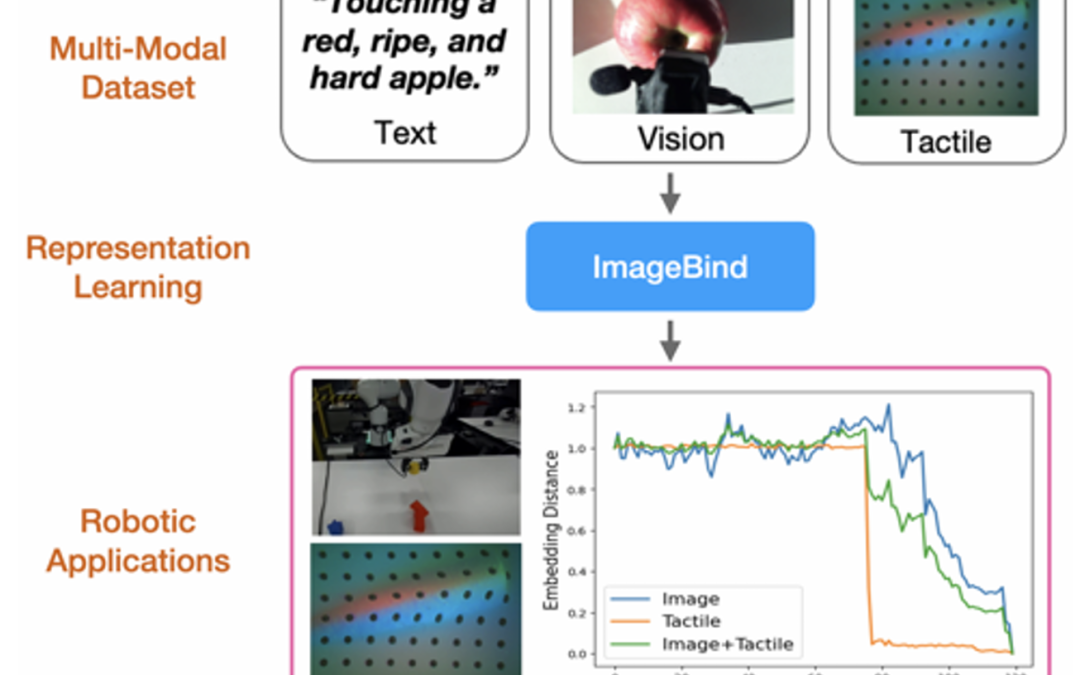
Advancements in embodied language models like PALM-E and RT-2 have significantly enhanced language-conditioned robotic manipulation. However, these advances remain predominantly focused on vision and language, often overlooking the pivotal role of...
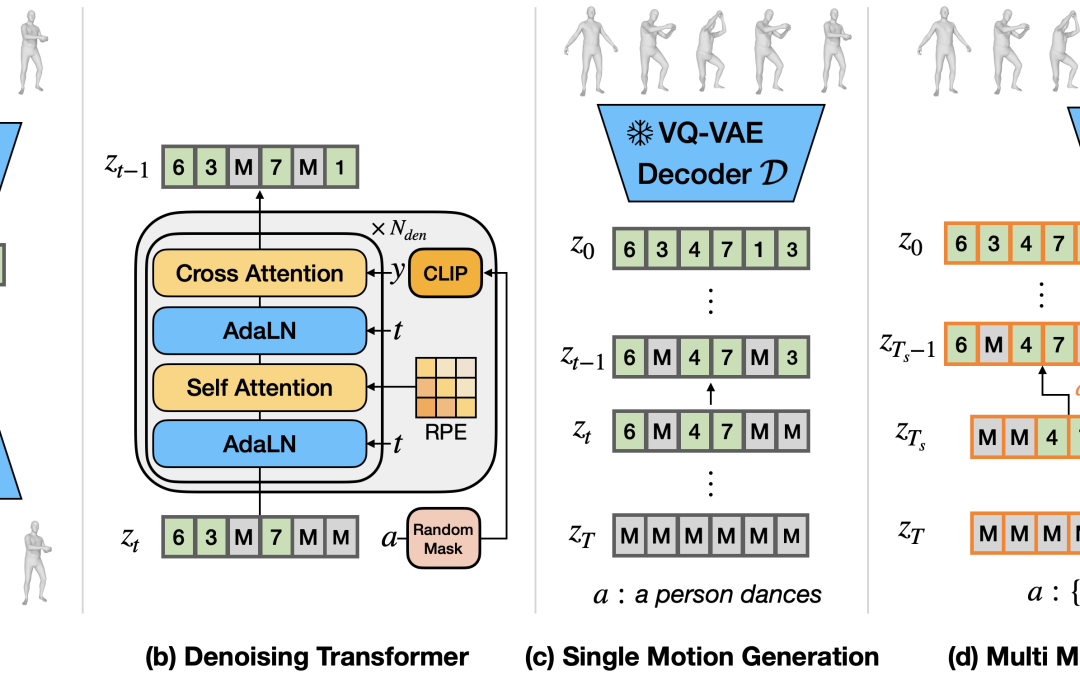
We introduce the Multi-Motion Discrete Diffusion Models (M2D2M), a novel approach for human motion generation from textual descriptions of multiple actions, utilizing the strengths of discrete diffusion models. This approach adeptly addresses the...
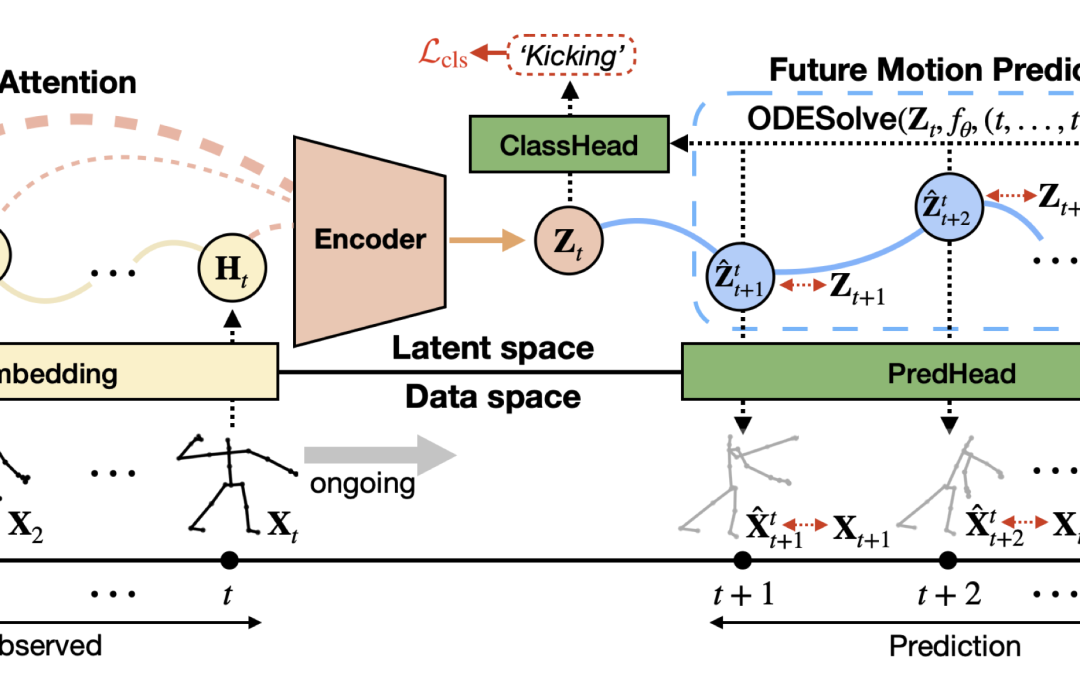
Skeleton-based action recognition has made significant advancements recently, with models like InfoGCN showcasing remarkable accuracy. However, these models exhibit a key limitation: they necessitate complete action observation prior to...
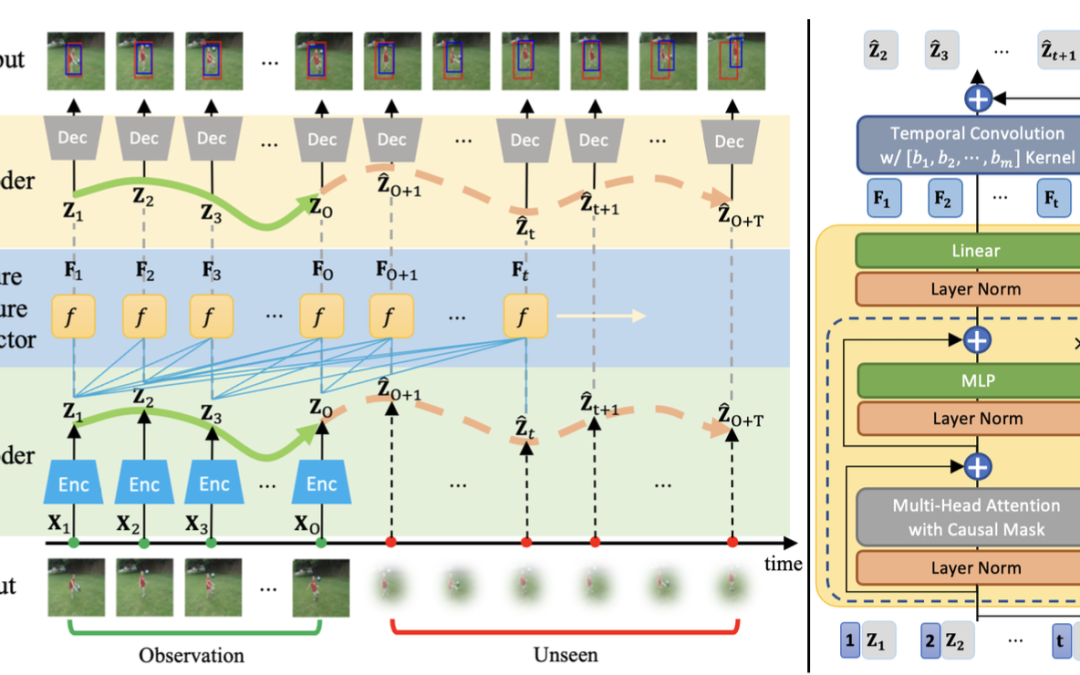
Predicting future action locations is vital for applications like human-robot collaboration. While some computer vision tasks have made progress in predicting human actions, accurately localizing these actions in future frames remains an area with...
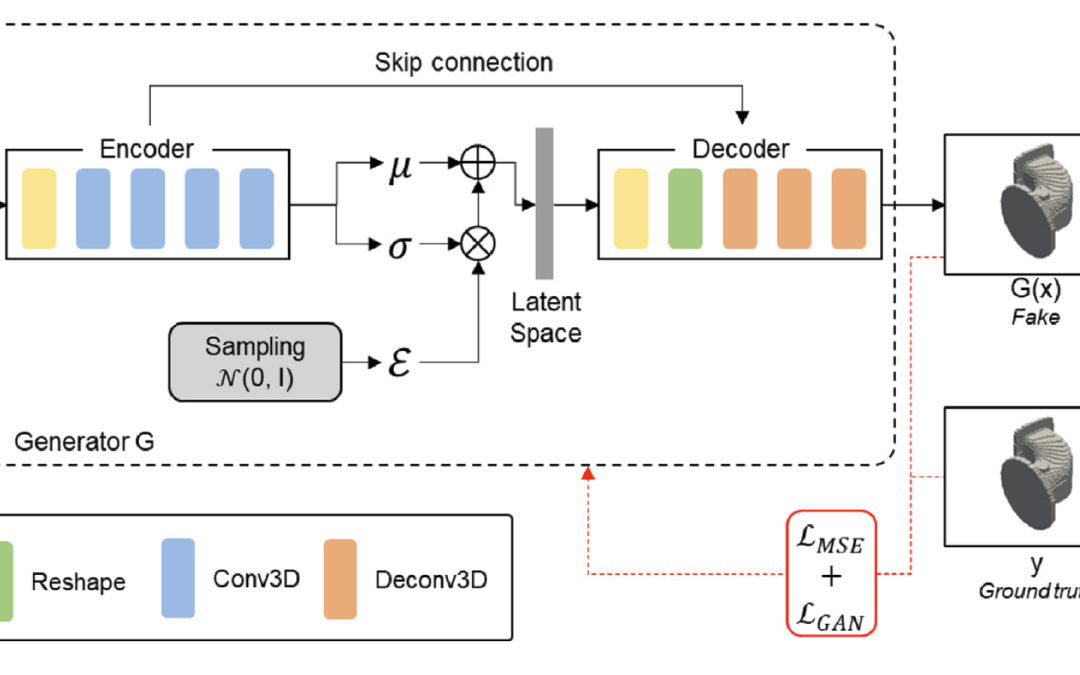
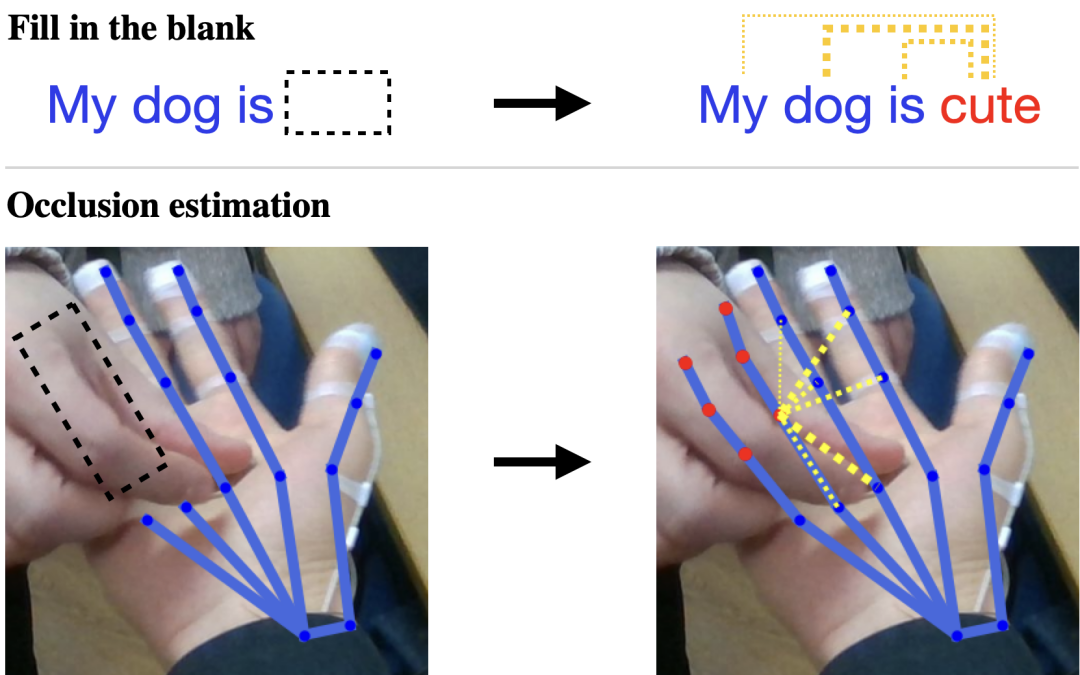
Accurately estimating the human pose is an essential task for many applications in robotics. However, existing pose estimation methods suffer from poor performance when occlusion occurs. Recent advances in NLP have been very successful in...

Human skeleton-based action recognition offers a valuable means to understand the intricacies of human behavior because it can handle the complex relationships between physical constraints and intention. Although several studies have focused on...
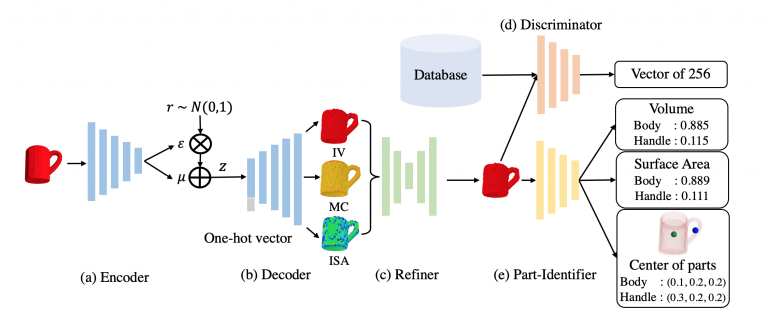

Abstract: First-person-view videos of hands interacting with tools are widely used in the computer vision industry. However, creating a dataset with pixel-wise segmentation of hands is challenging since most videos are captured with fingertips...