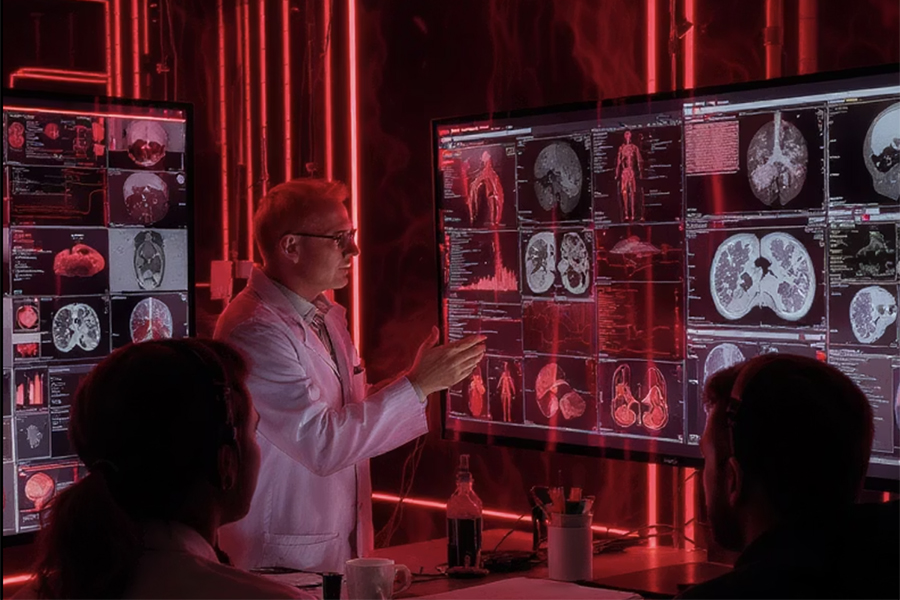
Center for AI and Robotic Excellence in medicine (CARE) | Autonomous Smart Laboratories
In recent years, research centers, universities, and industry have begun developing Self-Driving Laboratories (SDLs)—facilities that integrate AI-guided experimentation with automation and robotics. In SDLs, robotics execute experimental tasks while AI algorithms analyze data, validate or refute hypotheses, and uncover new scientific principles. This approach has already revealed insights into microbial community dynamics and advanced understanding of soft condensed matter and polymer physics. By pairing AI’s analytical power with the scalability and precision of robotics, SDLs accelerate the discovery of novel materials and enable complex molecular synthesis.
Building on this concept, the Living Autonomous Self-Driving Laboratory (ASDL) initiative seeks to create technologies, methods, and systems that make SDLs more flexible and adaptive across disciplines....
These laboratories will be capable of conducting diverse experiments with minimal human intervention, supported by self-reconfigurable machines that adapt their manipulators, sensors, and processes to new tasks. While much progress in SDLs has focused on inanimate materials, our primary contribution will be advancing manipulators, sensors, and intelligent mechanisms to handle living systems—ranging from individual cells to adult animal models.
Potential applications of ASDLs include:
- Autonomous Gloveboxes that provide protective barriers for pharmaceutical compounding.
- Organoid experimentation, such as autonomous assembly and biotic robotics.
- Ex-vivo culture of tumor tissue and the development of patient-derived organoids.
- Rapid, minimally invasive cellular extractionfrom live models (e.g., fin clipping in embryos to adults) with full survival.
- Automated experimentation with model organismssuch as zebrafish.
- High-throughput electrophysiology,including automated patch clamping at scale.
- Reverse translation platforms,enabling bedside-to-benchtop drug discovery and rapid therapeutic development.
Finally, this vision extends beyond stationary laboratories. Autonomous mobile laboratories—self-driving medical vehicles equipped with diagnostic systems—can bring advanced experimentation and care to remote, rural, and frontier settings. These vehicles would allow patients to access diagnostic devices independently, with oversight and continuous monitoring by AI expert systems.