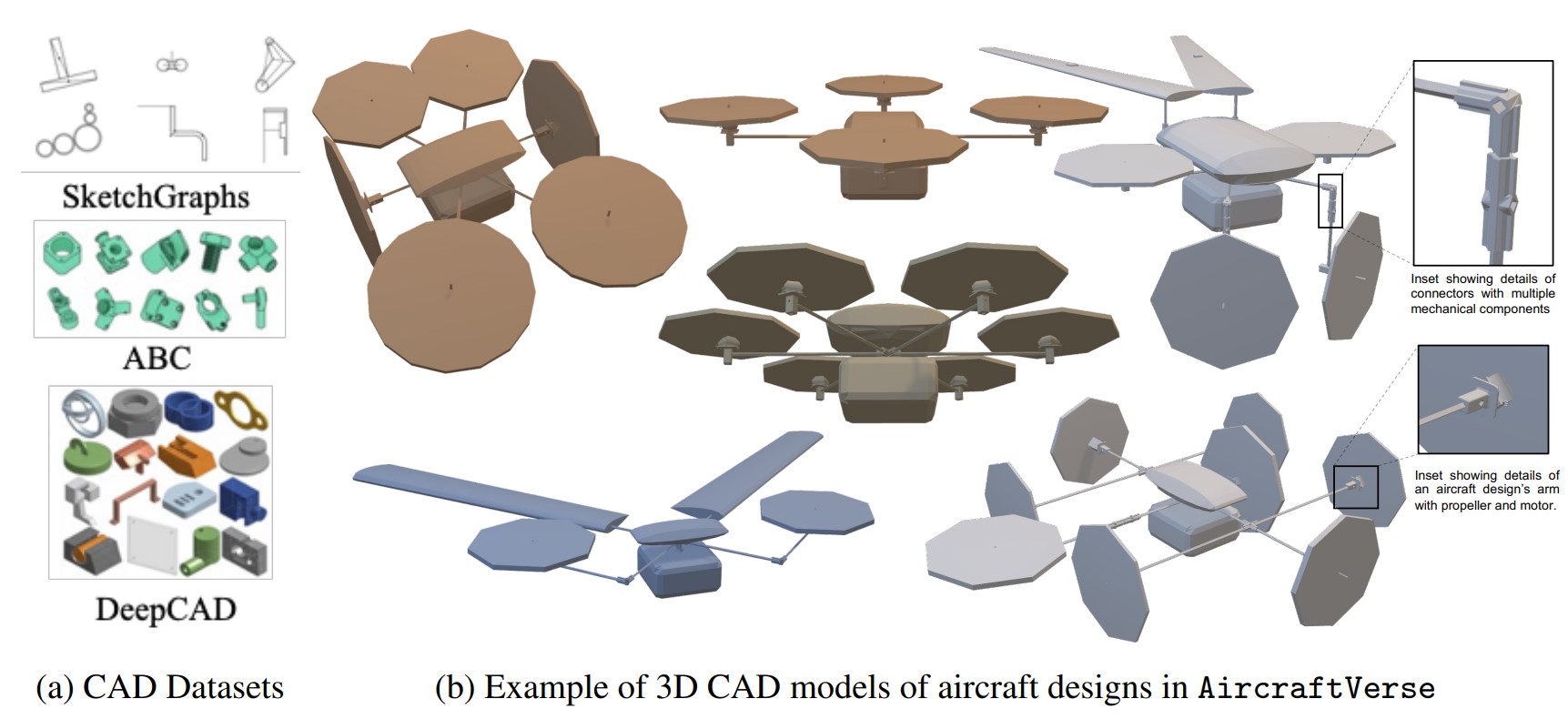
AircraftVerse: A Large-Scale Multimodal Dataset of Aerial Vehicle Designs

Karthik Ramani
Karthik Ramani is the Donald W. Feddersen Professor of School of Mechanical Engineering at Purdue University, with courtesy appointments in Electrical and Computer Engineering and College of Education. He earned his B.Tech from the Indian Institute of Technology, Madras, in 1985, an MS from Ohio State University, in 1987, and a Ph.D. from Stanford University in 1991, all in Mechanical Engineering. He has received many awards from the National Science Foundation (NSF) and other organizations. He has served in the editorial board of Elsevier Journal of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and the ASME Journal of Mechanical Design (JMD). In 2008 he was a visiting Professor at Stanford University (computer sciences), research fellow at PARC (formerly Xerox PARC). In 2016 summer he was visiting professor Oxford University Institute of Mathematical Sciences. He also serves on the Engineering Advisory sub-committee for SBIR/STTR for the NSF. In 2006 and 2007, he won the Most Cited Journal Paper award from CAD and the Research Excellence award in the College of Engineering at Purdue University. In 2009, he won the Outstanding Commercialization award from Purdue University. He was the co-founder of the world’s first commercial shape-based parts search engine (VizSeek) and more recently co-founded ZeroUI whose product (Ziro) won the Best of Consumer Electronics Show Finalist (CES 2016). His research interests are in the internet-of-things, augmented reality, modular and flexible robotic platforms, and human-machine interactions. His current projects include computer vision for object detection and grasp planning, modular robotic platform design, shape recognition using geometric deep learning, and physical reality simulation platform. His current research emphasis is to develop a Physical-Simulation Platform that will allow one to realistically simulate interactions between workers, robots, and machines in future workplaces such as factories and warehouses.
