
Psychrometric chambers go to -4°F
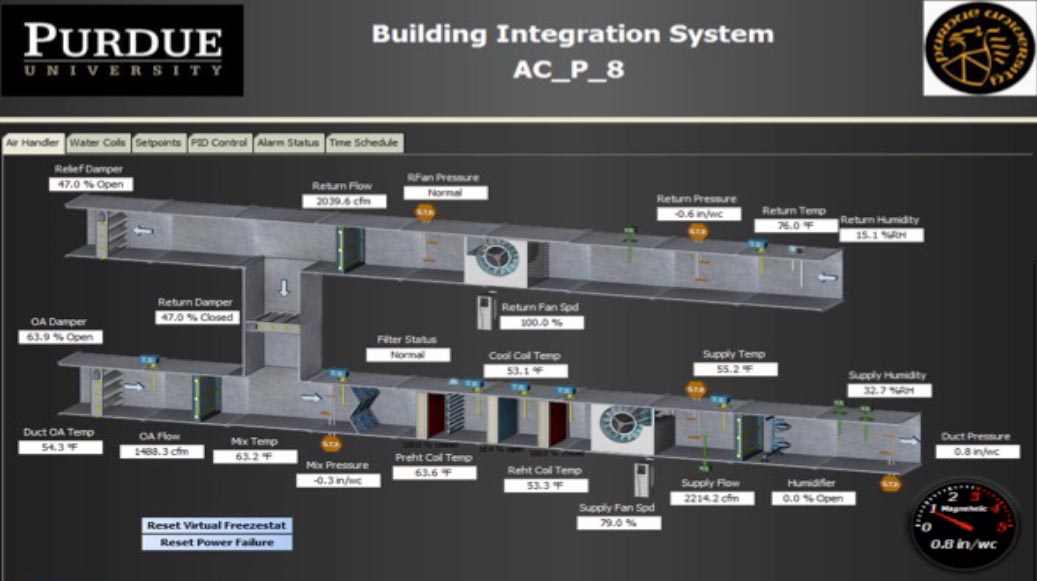
Herrick Labs' own HVAC system is monitored by hundreds of sensors

Geothermal bores go 300 feet deep

Prof. Qinyan Chen models the indoor air quality of an airline cabin at Herrick
A showcase for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning.
Since 1957, heating and refrigeration have been central to the mission of Herrick Labs. Today at Purdue, industry and academia join forces in one of the most advanced facilities of its kind. At the center of it all: six psychrometric chambers (3 pairs) for testing HVAC equipment:
- Each psychrometric room is 7000 cubic feet
- Capacity of 5 tons of refrigeration each (18 kW)
- Temperature range: -4°F to 130°F
- Designed to accommodate ASHRAE/ARI standard test procedures used in rating unitary air-conditioners and heat pumps
- Active desiccant dehumidification system to improve moisture removal at low ambient temperatures
Other facilities include:
- Psychrometric wind tunnel with dust injection system
- HVAC equipment lab with 90 ton centrifugal chiller and ice storage test facility
- Computer-controlled compressor load stands for small compressors
- Herrick Labs' own HVAC system is also a laboratory, with hundreds of sensors generating data
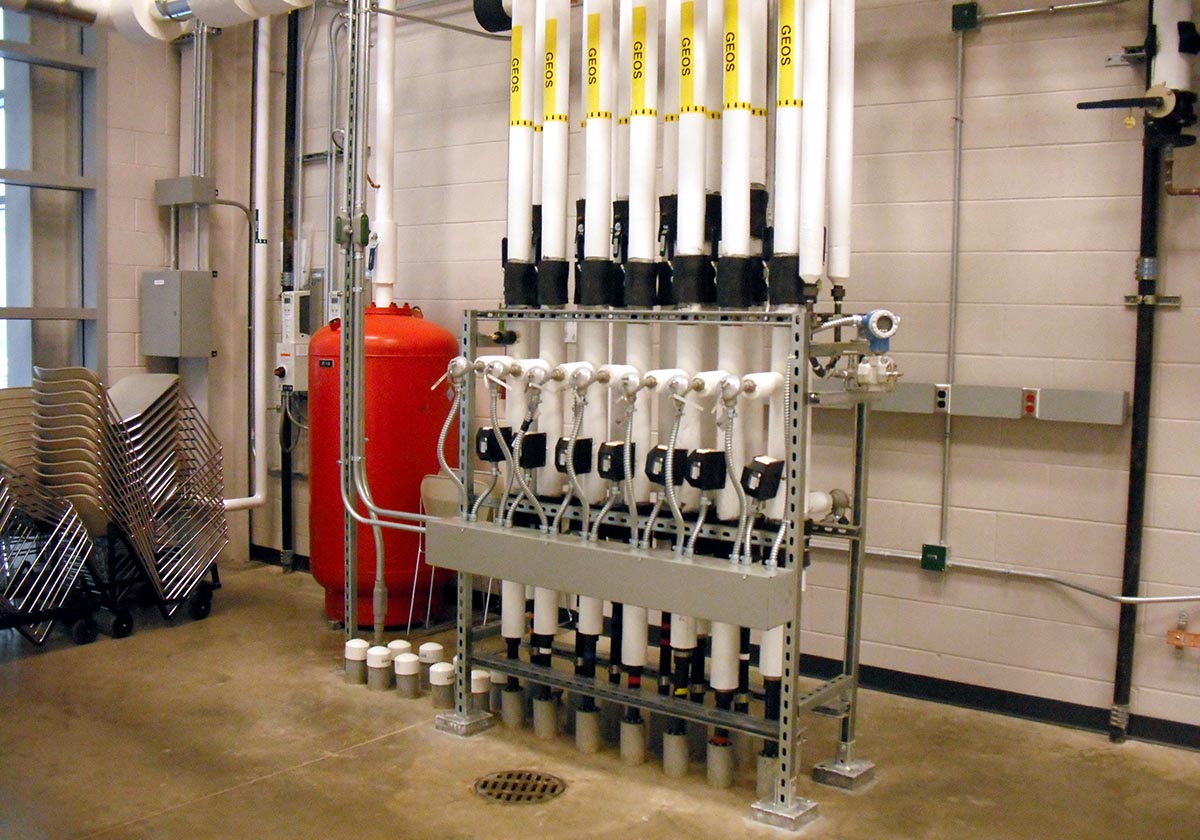
Geothermal
Herrick's geothermal field consists of 16 vertical U-tube heat exchangers with bores of 300 feet deep. The heat exchangers are instrumented to allow determination of ground heat transfer. One of the bores is instrumented with temperature sensors along its length to allow detailed model validation. Ground heat exchanger flow rates and inlet temperatures can be continuously varied to enable testing of advance control strategies.
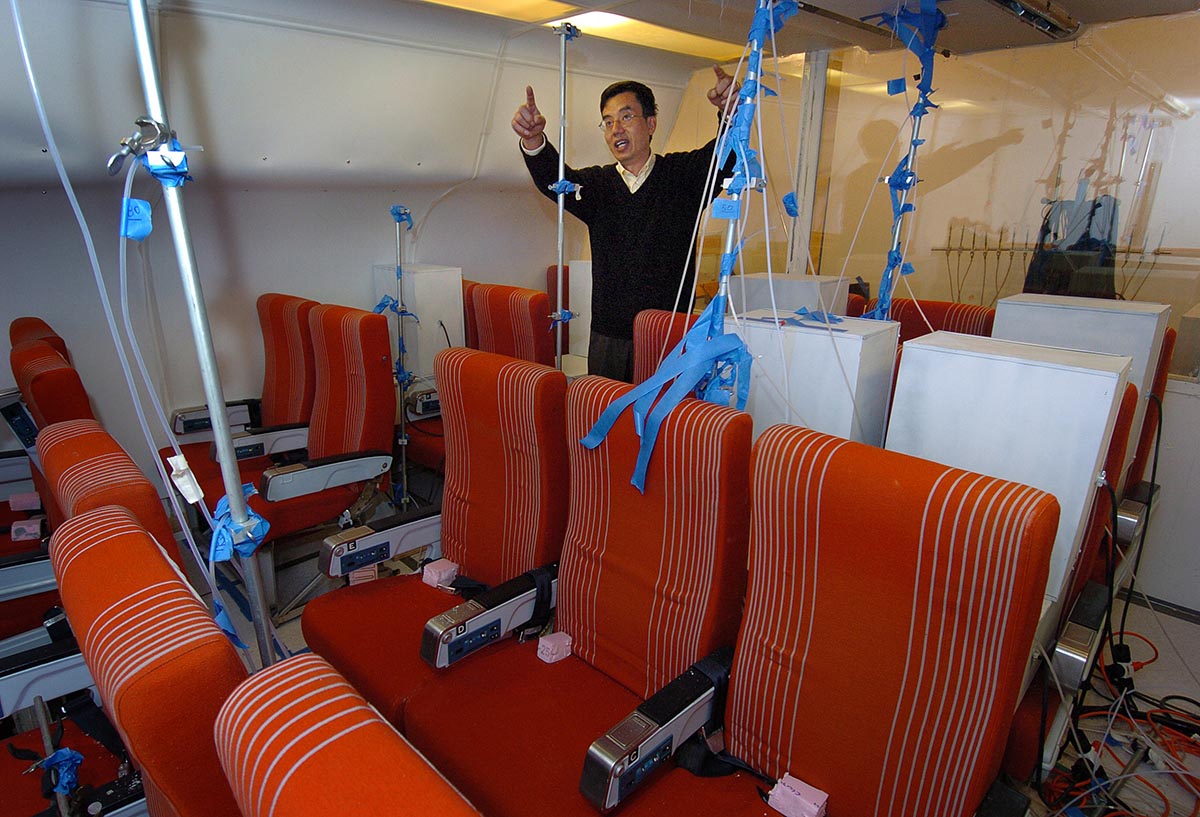
Indoor air quality
There are two indoor air quality (IAQ) laboratories that can simulate indoor and outdoor conditions. The indoor room is reconfigurable to allow air supply from ceiling, wall, or under-floor diffusers. It is also reconfigurable to simulate different types of indoor environments, such as homes, offices, classrooms, industrial workspaces, healthcare environments, aircraft passenger areas, and more. Measurements utilize:
- Particle image velocimetry (PIV) system to enable visualization of the flow field
- Tracer-gas sampler and chromatograph allowing 3-dimensional characterizations
- Ultrasonic and omni-directional anemometers
- Particle generators and analyzers, from a single nanometer to tens of micrometers in diameter
- Thermocouples and humidity sensors
These labs allow for controlled experimental studies on how people are exposed to indoor pollutants, and guide the creation of filtering and ventilation strategies to reduce exposure.
Herrick Labs • 177 S. Russell St., West Lafayette, IN 47907-2099 • (765) 494-2132 • hlab@purdue.edu
