Impact of Aging on the Thermophysical Properties of Lithium-Ion Battery Electrodes
Impact of Aging on the Thermophysical Properties of Lithium-Ion Battery Electrodes
| Event Date: | March 13, 2024 |
|---|---|
| Authors: | A. Marconnet, S. Herberger, S. Paarmann, P. Seegert, and T. Wetzel |
| Journal: | Journal of Power Sources |
| Paper URL: | Link to Full Text |
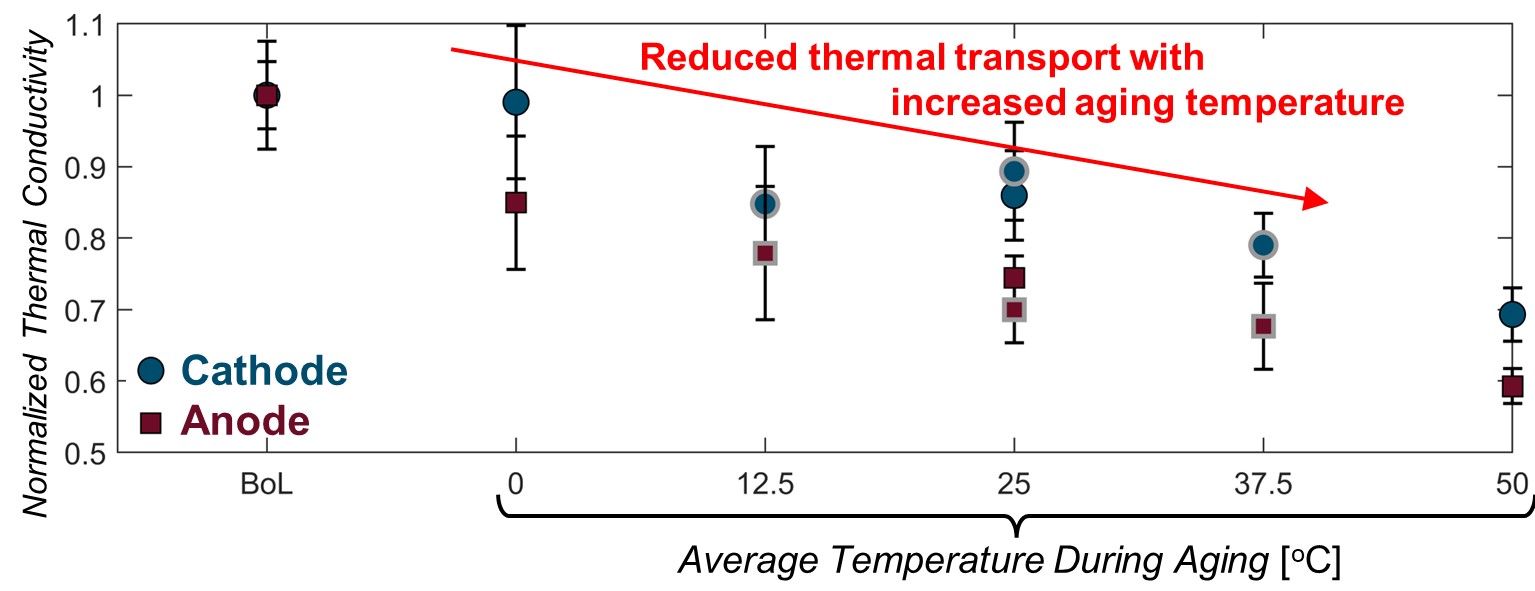
While battery researchers often focus on optimizing device performance to improve, for example, battery capacity or charging rate, thermal effects have often been relegated to a secondary concern. The evolution of the thermal properties with aging and cycling impacts the temperatures within the battery cell and, in turn, the performance and reliability of the battery cell. This work focuses on quantifying the change in thermophysical properties of lithium-ion battery cells subject to various aging conditions. The effective thermal diffusivity of the electrode stack and thermal conductivity of the active materials are significantly impacted by the aging conditions, while the volumetric heat capacity remains relatively constant. Aging below room temperature results in relatively stable thermal transport, while aging above room temperature degrades thermal transport by up to ~75% after 8200 equivalent full cycles at 50 ºC. For the cathode, the reduction in transport properties corresponds to visual observation of breakage of the particles. For the anode, solvent co-intercalation and exfoliation, along with growth of the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) and loss of contact between active particles, may explain the reduction. Ultimately, the changes in thermophysical properties with aging will increase temperatures and reduce the electrochemical performance and reliability.