Generative Photography
FlowSteer: Conditioning Flow Field for Consistent Image Restoration
Tharindu Wickremasinghe, Chenyang Qi, Harshana Weligampola, Zhengzhong Tu, Stanley H. Chan
Manuscript: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.08125
Project Page: https://tharindu-nirmal.github.io/FlowSteer/
Flow-based text-to-image (T2I) models excel at prompt-driven image generation, but falter on Image Restoration (IR), often “drifting away” from being faithful to the measurement. Prior work mitigate this drift with data-specific flows or task-specific adapters that are computationally heavy and not scalable across tasks. This raises the question “Can't we efficiently manipulate the existing generative capabilities of a flow model?” To this end, we introduce FlowSteer (FS), an operator-aware conditioning scheme that injects measurement priors along the sampling path,coupling a frozed flow's implicit guidance with explicit measurement constraints. Across super-resolution, deblurring, denoising, and colorization, FS improves measurement consistency and identity preservation in a strictly zero-shot setting-no retrained models, no adapters. We show how the nature of flow models and their sensitivities to noise inform the design of such a scheduler. FlowSteer, although simple, achieves a higher fidelity of reconstructed images, while leveraging the rich generative priors of flow models.
Seeing the Unseen World via 4D Dynamics-aware Generation
Yu Yuan, Tharindu Wickremasinghe, Zeeshan Nadir, Xijun Wang, Yiheng Chi, Stanley H. Chan
Manuscript: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.03350
Projet Page: https://yuyuanspace.com/SeeU/
Images and videos are discrete 2D projections of the 4D world (3D space + time). Most visual understanding, prediction, and generation operate directly on 2D observations, leading to suboptimal performance. We propose SeeU, a novel approach that learns the continuous 4D dynamics and generate the unseen visual contents. The principle behind SeeU is a new 2D-4D-2D learning framework. SeeU first reconstructs the 4D world from sparse and monocular 2D frames (2D-4D). It then learns the continuous 4D dynamics on a low-rank representation and physical constraints (discrete 4D - continuous 4D). Finally, SeeU rolls the world forward in time, re-projects it back to 2D at sampled times and viewpoints, and generates unseen regions based on spatial-temporal context awareness (4D-2D). By modeling dynamics in 4D, SeeU achieves continuous and physically-consistent novel visual generation, demonstrating strong potentials in multiple tasks including unseen temporal generation, unseen spatial generation, and video editing.
NewtonGen: Physics-Consistent and Controllable Text-to-Video Generation via Neural Newtonian Dynamics
Yu Yuan, Xijun Wang, Tharindu Wickremasinghe, Zeeshan Nadir, Bole Ma, Stanley H. Chan
Manuscript: https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.21309
Projet Page: https://yuyuanspace.com/NewtonGen/
A primary bottleneck in large-scale text-to-video generation today is physical consistency and controllability. Despite recent advances, state-of-the-art models often produce unrealistic motions, such as objects falling upward, or abrupt changes in velocity and direction. Moreover, these models lack precise parameter control, struggling to generate physically consistent dynamics under different initial conditions. We argue that this fundamental limitation stems from current models learning motion distributions solely from appearance, while lacking an understanding of the underlying dynamics. In this work, we propose NewtonGen, a framework that integrates data-driven synthesis with learnable physical principles. At its core lies trainable Neural Newtonian Dynamics (NND), which can model and predict a variety of Newtonian motions, thereby injecting latent dynamical constraints into the video generation process. By jointly leveraging data priors and dynamical guidance, NewtonGen enables physically consistent video synthesis with precise parameter control.
Generative Photography: Scene-Consistent Camera Control for Realistic Text-to-Image Synthesis
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2025
Yu Yuan, Xijun Wang, Yichen Sheng, Prateek Chennuri, Xingguang Zhang, Stanley Chan
Manuscript: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2412.02168
Projet Page: https://generative-photography.github.io/project/
Image generation today can produce somewhat realistic images from text prompts. However, if one asks the generator to synthesize a particular camera setting such as creating different fields of view using a 24mm lens versus a 70mm lens, the generator will not be able to interpret and generate scene-consistent images. This limitation not only hinders the adoption of generative tools in photography applications but also exemplifies a broader issue of bridging the gap between the data-driven models and the physical world. In this paper, we introduce the concept of Generative Photography, a framework designed to control camera intrinsic settings during content generation. The core innovation of this work are the concepts of Dimensionality Lifting and Contrastive Camera Learning, which achieve continuous and consistent transitions for different camera settings. Experimental results show that our method produces significantly more scene-consistent photorealistic images than state-of-the-art models such as Stable Diffusion 3 and FLUX.
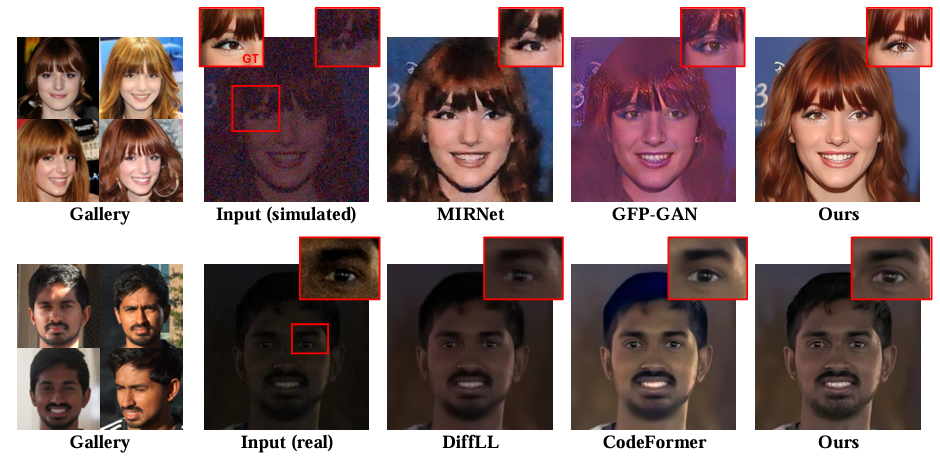
Personalized Generative Low-light Image Denoising and Enhancement
Xijun Wang, Prateek Chennuri, Yu Yuan, Bole Ma, Xingguang Zhang, Stanley Chan
Manuscript: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2412.14327
Project Page: https://genai-restore.github.io/DiffPGD/
While smartphone cameras today can produce astonishingly good photos, their performance in low light is still not completely satisfactory because of the fundamental limits in photon shot noise and sensor read noise. Generative image restoration methods have demonstrated promising results compared to traditional methods, but they suffer from hallucinatory content generation when the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is low. Recognizing the availability of personalized photo galleries on users’ smartphones, we propose Personalized Generative Denoising (PGD) by building a diffusion model customized for different users. Our core innovation is an identity-consistent physical buffer that extracts the physical attributes of the person from the gallery. This ID-consistent physical buffer provides a strong prior that can be integrated with the diffusion model to restore the degraded images, without the need of fine-tuning. Over a wide range of low-light testing scenarios, we show that PGD achieves superior image denoising and enhancement performance compared to existing diffusion-based denoising approaches.
Generative Quanta Color Imaging
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2024
Vishal Purohit, Junjie Luo, Yiheng Chi, Qi Guo, Stanley H Chan, Qiang Qiu
Manuscript: https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.19066
Project Page: https://vishal-s-p.github.io/projects/2023/generative_quanta_color.html
The astonishing development of single-photon cameras has created an unprecedented opportunity for scientific and industrial imaging. However the high data throughput generated by these 1-bit sensors creates a significant bottleneck for low-power applications. In this paper we explore the possibility of generating a color image from a single binary frame of a single-photon camera. We evidently find this problem being particularly difficult to standard colorization approaches due to the substantial degree of exposure variation. The core innovation of our paper is an exposure synthesis model framed under a neural ordinary differential equation (Neural ODE) that allows us to generate a continuum of exposures from a single observation. This innovation ensures consistent exposure in binary images that colorizers take on resulting in notably enhanced colorization. We demonstrate applications of the method in single-image and burst colorization and show superior generative performance over baselines.