Recent Projects
These are the most recent research projects developed or in progress at RVL.
For a comprehensive list of all RVL projects, please visit our Project Archive.
- Research in Wireless Camera Networks
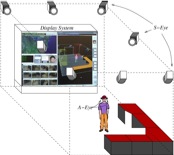
The Purdue-Olympus A-Cubed Project Wireless camera networks are more complex than wireless sensor networks simply because cameras generate a lot more information than simple scalar sensors and also because cameras are directional - 3D Modeling of Dormant Apple Trees
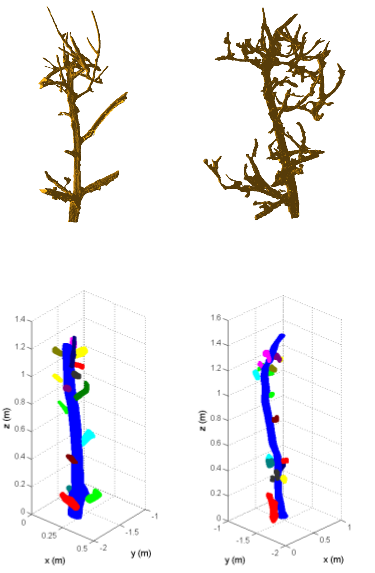
The USDA Automatic Pruning Project Dormant pruning is one of the most costly and labor-intensive operations in specialty crop production. During winter, a large crew of trained seasonal workers has to carefully remove the branches from hundreds of trees using a set of pre-defined rules. - Object Tracking Using a Wireless Camera Network
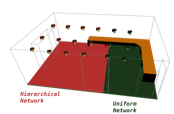
Conventional camera networks require an infrastructure of cables and computers to transmit, store and process the information coming from the cameras. - Object Tracking on SIMD-based Smart Cameras

Using Parallel Histogram-based Particle Filter As the demand for low-power, portable, and networked computing devices continues to increase, it is natural that the number and the complexity of services provided by such devices will only grow. - Tracking Humans with a Wired Camera Network

The ability of machines to detect humans and recognize their activities in an environment is an essential part of allowing a machine to interact with humans easily and efficiently. - The Intelligent Shelf Project

Real-time face pose estimation Faces are central to the visual component of human interaction. Classic examples of this include face recognition and visual focus of attention (V-FOA) analysis. - Distributed and Light-weight Multi-Camera Human Activity Classification

Multiple view action recognition is a logical next step to fixed-view action recognition because it addresses a more realistic scenario: it does not assume that humans are performing the action in a specific direction relative to the camera, e.g. frontal or profile views. In addition, capturing an action from multiple views obtains additional features of the action, thereby potentially increasing the discriminative power of the recognition algorithm. - An Approach-Path Independent Framework for Place Recognition and Mobile Robot Localization in Interior Hallways

This work is about self-localization by a robot using stereo images of the environment. We use 3D-JUDOCA features that have high robustness to viewpoint variations. We present a novel cylindrical data structure — the Feature Cylinder — for expediting localization with two hypothesize-and-verify frameworks. - Combined Object Segmentation and Tracking

Many object tracking algorithms implicitly or explicitly use a coarse segmentation of each target object using a simple mask such as a rectangle or an ellipse. This coarse segmentation results in several problems in tracking. If the mask is too large, extra background pixels will be included causing target drift. - Tracking and Segmentation on the CLIF2007 Dataset

Our previous work showed that combining segmentation and tracking gives improved tracking performance compared to bounding-box approaches. The key idea is to define a probability distribution over the pixels belonging to each of the targets and the background. - Ground Target Localization
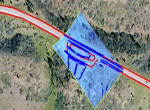
Based on Landmark registration in aereal images The aim of this project is to provide the accurate location of ground objects in a world coordinate system using vision-enabled unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). Our approach pursues to find the correct registration between aerial images and reference image. - Line Tracking for Assembly-on-the-fly
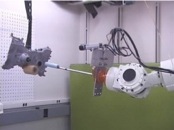
The goal of this project is to develop a vision-guided robotic system that can operate on a moving assembly line. - Distributed Online Localization of Wireless Camera-based Sensor Networks by Tracking Multiple Moving Objects
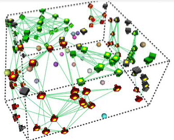
A typical wireless sensor network consists of a large number of sensor nodes densely deployed in the field, each equipped with wireless communication, sensing and computing capabilities with a limited power resource. - Sensor Selection Problem in Large Camera-Based Sensor Networks
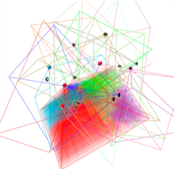
Modern navigation, mapping and surveillance systems require numerous vision sensors to be mounted at random locations over a geographically large area. - 3D Tracking of 3D Rigid Objects with Direct Image Alignment and Local Appearance Based Feature Matching

We demonstrate how by combining the notion of modular eigenspaces with multiple keyframes, an image-alignment based tracking algorithm can be made to accommodate large variations in 3D pose. - Model-Based 3D Rigid Objects Tracking

The goal of this work is to develop a visual object tracking system that can give accurate 3D pose -- both position and orientation in 3D Cartesian space -- of a rigid object. - Content-Based Image Retrieval from large Medical Image Databases
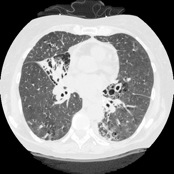
Content-based Image Retrieval (CBIR) consists of retrieving the most visually similar images to a given query image from a database of images. - Multimedia Database for Self-diagnosis of skin lesions
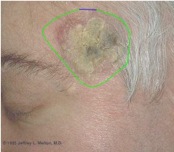
This project explores a novel approach to web-based self-diagnosis using multimedia databases. - Interactive Image Segmentation
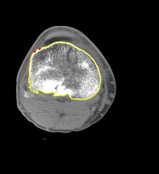
Segmentation is an important computer vision problem. Despite intensive research for several decades, the problem stubbornly insists on being unsolved for arbitrary images. - Computer Vision for Recognition of American Sign Language

This project offers a novel approach to the problem of automatic recognition, and eventually translation, of American Sign Language (ASL). - Robust Motion Estimation under Varying Illumination
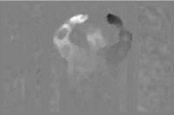
The optical-flow approach has emerged as a major technique for estimating scene and object motion in image sequences. However, the problem of motion estimation, in general, is made difficult by large illumination variations and by motion discontinuities. - Person Following using a Vision-Guided Mobile Robot

We have developed a person following mobile robot with maintaining a constant distance from a person using two cameras each of which has its own pan/tilt unit (PTU). - Illumination Invariant Color Representation

The goal of this project is to develop a color space transformation technique that adapts the color space to the color of the illuminant and leads a new color representation that is more independent of the illumination intensity and is more adapted to the spectral composition of the illumination than any of the existing approaches. - Hierarchical Data Structure for Real-Time Background Subtraction

One of the drawbacks of background subtraction methods for motion detection is a slow processing time. Consequently, real-time motion detection at 30 frames per second with an image size of 480 by 640 is not possible with these methods. - Segmentation of Apple Fruit from Video via Background Modeling

The cost of labor for orchard tasks currently accounts for over 50% of orchardists' costs. In addition, the seasonal nature of many orchard tasks and high volume of workers needed results in a shortage of labor, especially for harvest work. - 3D Modeling of Optically Challenging Real-World Objects

One of the challenges in 3D modeling results from the fact that many real-world objects have surface materials that are not ideal for optical range sensors. - Managing Complexity of Large/Ultra Large Software System
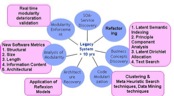
SLIM Today there exist many important applications in business and commerce that consist of millions of lines of code that are becoming increasingly difficult to maintain.