Tuning Inter-Particle Contacts and Transport Properties of Maghemite-Thermoset Nanocomposites by Applying Oscillating Magnetic Fields
Tuning Inter-Particle Contacts and Transport Properties of Maghemite-Thermoset Nanocomposites by Applying Oscillating Magnetic Fields
| Authors: | M. Spencer, A. Alsaati, J.E. Park, R. Braga Nogueira Branco, A.M. Marconnet, and N. Yamamoto |
|---|---|
| Journal: | ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces |
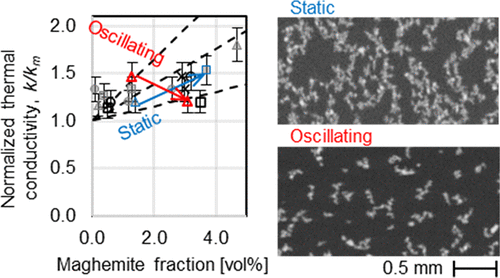
Conductive nanofillers, if integrated in an organized manner, can improve the transport properties of polymer matrices without compromising on their light weight. However, the relationship between the particle assemblies and transport properties of such nanocomposites, especially the competing effects of connected nanofiller pathways compared to resistances at interparticle contacts, has not been quantitatively studied. In this work, with the model nanocomposite of maghemite nanoparticles in epoxy, a novel fabrication method has been demonstrated to align nanofillers and control the interparticle contact amount within such a nanofiller assembly, using nanoparticle surface functionalization and oscillating magnetic field application. The nanofiller assembly cross-sectional areas were measured by processing micro-CT images and compared with the measured electrical and thermal properties of the nanocomposites. In terms of thermal transport, when the nanofiller assembly cross-sectional area was small, the dominance of conductivity pathways was observed up to ∼4.7 vol %, while interfacial thermal resistance began to dominate when the nanofiller assembly cross-sectional area became larger than 2700 μm2.