Bowen Lab Projects
Past Projects
News
Teaching Machines to Classify and Organize Reconnaissance Image Data
November 20, 2018
News
Resilient ExtraTerrestrial Habitat Engineering (RETH)
October 22, 2018
News
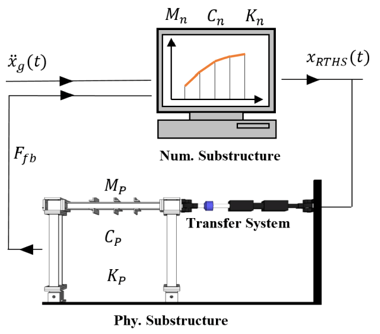
Establishing a Research Network in Hybrid Simulation for Multi-Hazard Engineering
September 10, 2018
News
Probability of Detection Study for Bridge Inspection Related to Steel Bridges
July 30, 2018
News
Seismic Response of Structural Walls with Reinforcement and Geometric Discontinuities
March 12, 2018
News
Seismic Response of Reinforced Concrete Walls with Lap Splices
October 24, 2017
News
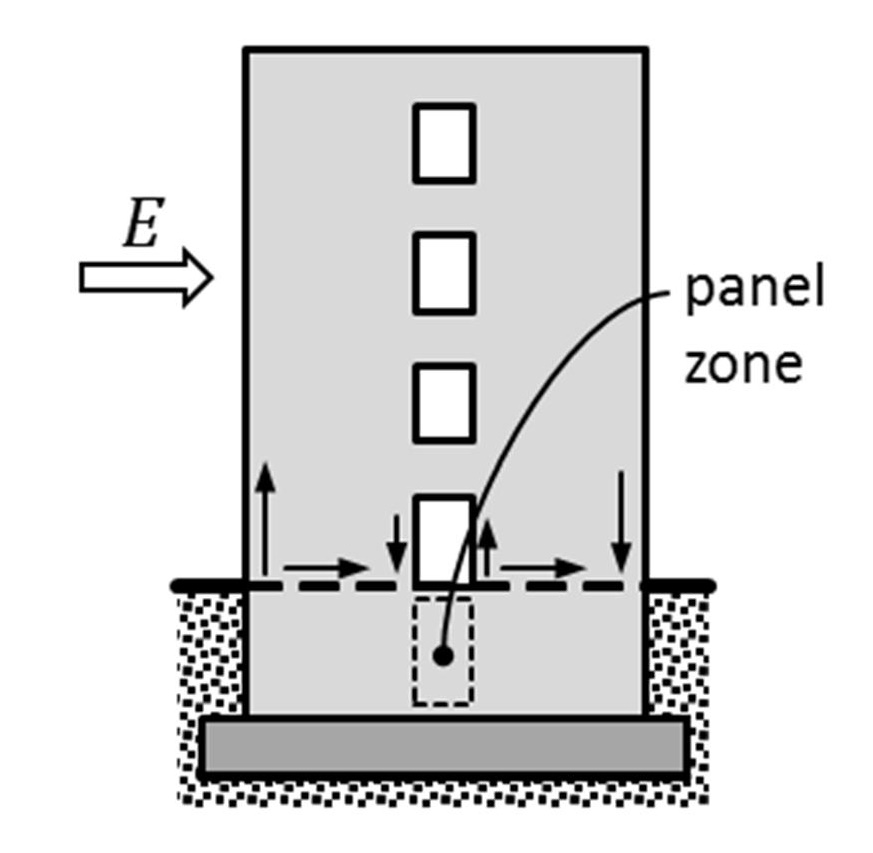
Member-level Redundancy in Built-up Steel Members
October 02, 2017
News
Modal Analysis and Load Identification Techniques for a Rapidly Emplaced Bridge System
September 19, 2017
News
US-China: Verification of Real-Time Hybrid Simulation Through Shake Table Comparison
September 01, 2017
News
Solar Cooling and Heating System
August 08, 2017
News
NEES Data Flow Testbed
August 01, 2017
News
Laboratory Testing of Railroad Flatcars For Use as Highway Bridges on Low-Volume Roads to Determine Ultimate Strength and Redundancy
July 21, 2017