AI/ML Biocatalytic Pathway Design and Synthesis
AI/ML Biocatalytic Pathway Design and Synthesis

The combination of AI and traditional search techniques are being employed to efficiently assess the literature, identify technologies and gaps, and anticipate future developments for cascades of enzymes or batch bioreactors for chemicals manufacture. This includes recycling plastics, energetic materials, and feedstocks for low carbon footprint fuels.
The research is being initiated with a state of technology assessment (SOT) performed by human experts with experience in enzyme-based biomanufacturing while being complemented by AI. This work is shaping the questions and then follow up the suggestions given by AI. Manual review of the scientific literature including published papers and patents is utilized to ensure ensure the scientific rigor of the final assessment. The results from our assessment are being compared to preliminary reverse synthesis, i.e., AI /ML guided design of enzyme catalysts with preliminary work on generating the predicted enzyme structures and activities using microbial hosts that have been modified using either synthetic biology or recombinant methodology.
The SOT evaluation will emphasize the search for and identification of enzyme technologies that have potential to evolve into Biomanufacturing Readiness Level (BioMRL) 4 to BioMRL 7 readiness, and therefore could quickly be deployed to initiate expansion of the biomanufacturing sector in the US. Purdue will engage local and regional community partners to identify opportunities for expanding industrial and defense-related biomanufacturing and workforce development while providing a comprehensive assessment of current status, gaps and future directions of enzyme-based biomanufacturing.
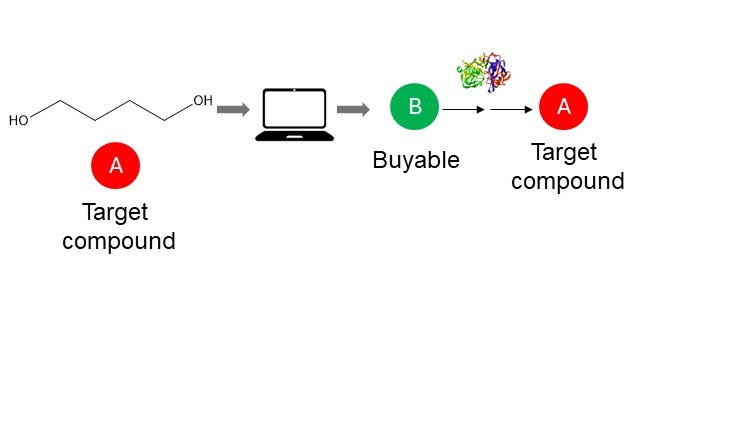
AI will be used for structure prediction and enzyme design and employ examples of computationally designed enzymes that catalyze chemical transformations useful for commercially producing the 10 target molecules. In these selected examples, either structure prediction or computational enzyme design will inform the experimental development commercial scale biocatalytic processes. In some examples, enzyme structure prediction will inform amino acid residues to target for protein engineering. In other examples, de novo computational enzyme design will generate enzyme candidates with desired catalytic activity.
Enzymes can be obtained from a variety of sources, including whole microorganism and recombinant proteins produced in heterologous host such as Escherichia coli. Here, Purdue will review the use of enzymes in a variety of different preparations, including whole cells and isolated enzymes. Purdue will also discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each preparation type.
LORRE researchers will explore gene synthesis and enzyme production using fermenters to support both whole organism and isolated enzyme biocatalysis. Then, LORRE will identify and describe the separation technology for purifying enzymes (e.g., affinity chromatography, ion-exchange chromatography) for application in isolated enzyme biocatalysis.
