Resources from publications in our group
MATLAB based parallel computing methods for parameter calibration and spatial optimization <Top> |
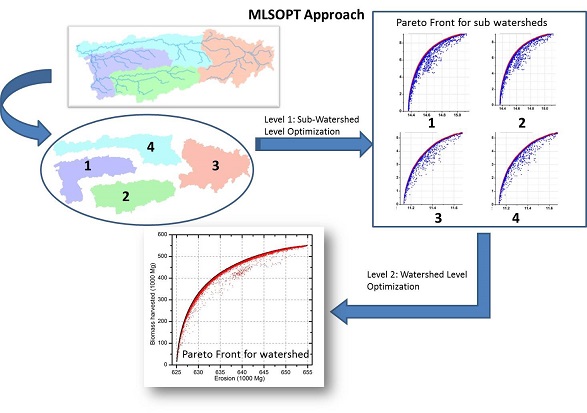
Simple parallel computing methods were developed using the ‘spmd’ and ‘parfor’ functions of MATLAB and tested with two case studies for parameter calibration and spatial optimization using the SWAT model (Soil and Water Assessment Tool: http://swat.tamu.edu/) (Her et al., 2015). The case study demonstrated that the methods could save time required to complete the optimization tasks by 80% when using the AMALGAM optimization algorithm (Vrugt and Robinson, 2007: http://faculty.sites.uci.edu/jasper/sample/). The methods do not require any source code modification of hydrologic simulation model used, thus can be adapted to any model. More details can be found in Her et al (2015). Submit request form to obtain a set of sample MATLAB codes used for the tests. MLSOPT approach is developed for efficiently solving complex watershed scale optimization problems. The method works at two levels: a watershed is divided into small sub-watersheds and optimum solutions for each sub-watershed are identified individually. Subsequently sub-watershed optimum solutions are used for watershed scale optimization. Tested results from case studies indicated that the MLSOPT approach is robust in convergence and computationally efficient compared to the traditional single-level optimization frameworks. The MLSOPT was 20 times computationally efficient in solving source area based optimization problem while it was 3 times computationally efficient for watershed outlet based optimization problem compared to a corresponding single-level optimizations. More details can be obtained from Cibin and Chaubey (2015, doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2014.12.014). You can request the MATLAB codes of MLSOPT with case study examples via request form.
|
Multi-level spatial optimization (MLSOPT) approach for watershed scale spatial optimization <Top> |
MLSOPT approach is developed for efficiently solving complex watershed scale optimization problems. The method works at two levels: a watershed is divided into small sub-watersheds and optimum solutions for each sub-watershed are identified individually. Subsequently sub-watershed optimum solutions are used for watershed scale optimization. Tested results from case studies indicated that the MLSOPT approach is robust in convergence and computationally efficient compared to the traditional single-level optimization frameworks. The MLSOPT was 20 times computationally efficient in solving source area based optimization problem while it was 3 times computationally efficient for watershed outlet based optimization problem compared to a corresponding single-level optimizations. More details can be obtained from Cibin and Chaubey (2015, doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2014.12.014). You can request the MATLAB codes of MLSOPT with case study examples via request form.
|
Map of marginal land suitability for growth of switchgrass, Miscanthus and hybrid poplar <Top> |
This map describes the suitability of margianl land for growth of three potential bioenergy crops. The suitability was evaluated using a fuzzy logic based framework written in python code (download). Here is a preview of map for switchgrass.
|
Contact: ichaubey@purdue.edu
Phone: 765-494-5013
Fax: 765-496-1115
225 South University St., Purdue University
West Lafayette, IN 47907