DEBISim (Dual Energy Baggage Image Simulator):
A Python-based 3D CT Simulation library for Single and Dual energy X-ray image data generation.
This library is designed to aid in the development, testing and evaluation of Single and Dual Energy CT based target detection systems for airport baggage screening and other CT imaging applications requiring anomaly detection.
DEBISim (Dual Energy Baggage Image Simulator) is a Python-based 3D CT Simulation library for Single and Dual energy X-ray image data generation. This library is designed to aid in the development, testing and evaluation of Single and Dual Energy CT based target detection systems for airport baggage screening and other CT imaging applications requiring anomaly detection. The software package presents a simulation pipeline for developing algorithms for baggage inspection scanners and in other similar security screening applications. CT-based target detection systems in general require generating testing and training data by packing and scanning a large number of real bags with real threat materials. Since DEBISim incorporates a complete simulation of physical phenomena involving X-ray transmission, attenuation and detection and also provides a user-configurable scanner geometry, it is an alternative to physically scanning CT baggages for data generation. DEBISim also knows about the wide range of materials (and threat materials) that are encountered in a scanned bag and includes support for simulating them while packing virtual bags.
The DEBISim package includes the following features:
The code for DEBISim contains four main modules, RandomizedModeGUI, UserInteractiveModeGUI, DEBISimPipeline and DEBISimDatasetGenerator, as well as seventeen support modules written by us. DEBISim also uses the following four third-party open source libraries: FreeCT_wFBP, ASTRA-toolbox, Gpufit and the NIST XCOM Photon Cross-Sections Database. The setup and installation of these third-party libraries is described in Setup and Installation while the details of their operation can be found in the Documentation.
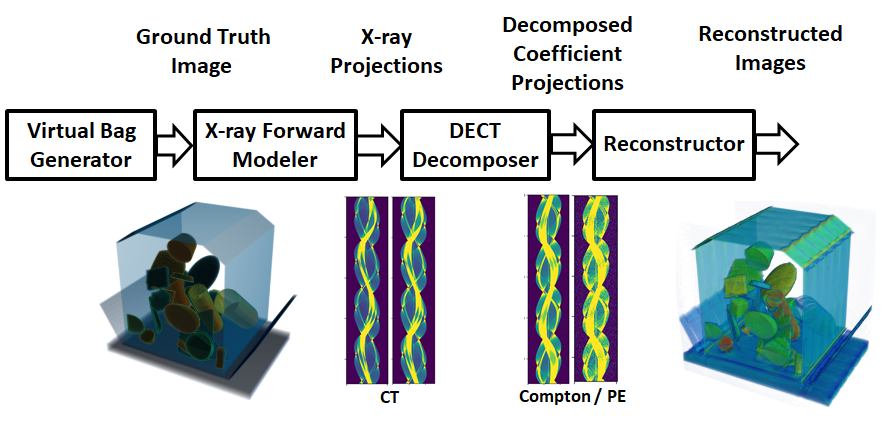
As shown in the figure below, the four basic building blocks of the DEBISim simulation pipeline are: (i) Virtual Bag Generator, (ii) Forward X-ray Modelling, (iii) DE Decomposer and (iv) Reconstructor.

Generating both projection and reconstruction data using DEBISim requires executing all of the four blocks in the order as shown above. Here is a brief introduction to the blocks (their details are presented in the Documentation):
Virtual Bag Generator Block:
This block generates a virtual volumetric bag that contains user-specified objects with user-specified shapes and material properties. The block also includes facilities for a 3D visualization of the bag. Virtual bags can be generated either in a user-interactive mode or automatically through a randomized procedure. Note that even when the bags are generated randomly their properties can be set by the user.
Forward X-ray Modelling Block:
Based on the user's selection of the X-ray scanner, the forward X-ray modelling block calculates the projections of the virtual bag for the imaging geometry. Taking into account the user-specified X-ray scanner geometry, DEBISim employs the ASTRA toolbox for generating the projection data.
Dual Energy Decomposition Block:
This block is used for processing the dual energy CT projections generated by the forward modelling block in order to extract the DECT coefficient line integrals. Depending on the basis function used for DECT decomposition, the line integrals will correspond to different pairs of material properties. For example, a commonly used pair is the Compton-Photoelectric Coeeficient.
Reconstructor Block
This block creates 3D CT reconstructions from the dual energy X-ray projection data. These reconstructions by default are for Photoelectric and Compton coefficient parameters but can easily be transformed into other material properties such as the effective atomic number and electron density.
Further information on each of the blocks as well as how to run the pipeline can be found in the Documentation.
DEBISim is designed to run on Linux/MacOSx OS machines. Make sure that the aforementioned third-party modules need to be pre-installed on the machine before running DEBISim. Guidelines for installing these have been described in Setup and Installation.
The system pre-requisites for DEBISim are:
See Setup and Installation on instructions for meeting these requirements.
DEBISim can be downloaded using one of the following links - make sure that the steps in Setup and Installation have been performed before running the software:
Public Domain, Copyright © 2018, Robot Vision Lab, Purdue University.
All publications using DEBSim or its datasets must cite the following paper:
@article{manerikar2021debisim,
title={DEBISim: A simulation pipeline for dual energy CT-based baggage inspection systems},
author={Manerikar, Ankit and Li, Fangda and Kak, Avinash C},
journal={Journal of X-Ray Science and Technology},
volume={29},
pages={259--285},
year={2021}
}
DEBISim has been created by Ankit Manerikar, Fangda Li, Tanmay Prakash and Avinash Kak at the Robot Vision Lab, Purdue University, USA.
The authors may be contacted at: amanerik@purdue.edu (Ankit Manerikar) and li1208@purdue.edu (Fangda Li).