Single Stage Centrifugal Compressor (SSCC)
|
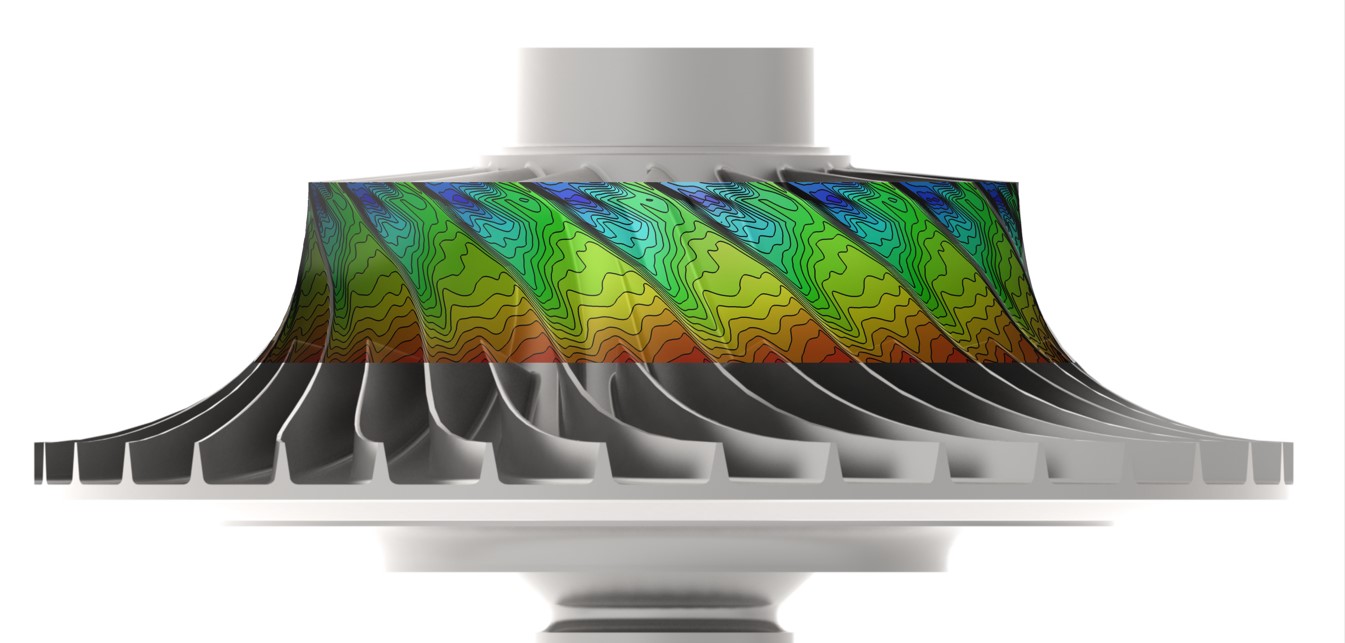
A single-stage centrifugal compressor designed by Honeywell has been installed at Purdue University to contribute to the experimental database on high-speed, high-pressure ratio centrifugal compressor performance. The rig, which operates at a design speed of 45,000 rpm and a pressure ratio greater than 6, has been extensively instrumented to provide steady and unsteady aerodynamic and aeromechanics data which will be used for tool development and validation. All current work with the Purdue SSCC rig is funded by Honeywell Aerospace. |
|
Current work: Inlet distortion effects on centrifugal compressor aerodynamics
Experimental investigation of tip clearance effects
|
|
The SSCC compressor is heavily instrumented with over 500 data collection channels for health monitoring and performance, with devices such as pressure transducers, thermocouples, capacitance probes, light probes, and strain gauges. Total temperature/total pressure rakes at the compressor inlet and exit provide information for stage performance data. Unsteady Instrumentation Kulite pressure transducers placed along the impeller shroud, vaneless space, and diffuser vanes measure unsteady pressure fluctuations resulting from impeller blade passage. Strain gauges measure the dynamic strain on the impeller. A slip ring translates their signals from the rotating to the stationary reference frame. The strain gauges and Kulite pressure transducers are simultaneously sampled at up to 1 MHz for detailed characterization of unsteady flow phenomena. Additionally, the rig is instrumented with NSMS light probes to measure blade deflections. Clearance Control The SSCC rig has an active clearance control system and can actuate the impeller at any speed to take a constant clearance map. Clearances are monitored in real-time by capacitance probes mounted at the inducer, knee, and exducer and are recorded to a resolution of 0.0001”. Bleed Flow System Ports at the impeller backface and on the shroud near the diffuser inlet are independently controlled in the SSCC's secondary air system. The bleed flows are measured with separate calibrated venturi meters to quantify the mass flow as a fraction of the bulk flow. Optical Access Windows in both inlet configurations enable LDV techniques to capture three-dimensional velocity fields upstream of the impeller leading edge. |
Theses
|
 Research Objectives
Research Objectives Specific Instrumentation Capabilities
Specific Instrumentation Capabilities