 Digital Mammography Research at Purdue University
Digital Mammography Research at Purdue University Digital Mammography Research at Purdue University
Digital Mammography Research at Purdue UniversityBreast cancer is one of the leading causes of death in women. Studies have indicated that cure rates dramatically increase if the breast lesion can be detected at a size less than 1 centimeter, which is too small for the lesion to be palpable. The only way a lesion this small can be detected is through screening mammography. Our goal has been to develop computer-aided diagnostic techniques for automatic detection and classification of breast tumors. This research is led by Prof. Edward J. Delp at the Video and Image Processing Laboratory (VIPER).
| Microcalcifications |  |
| Circumscribed Lesions | 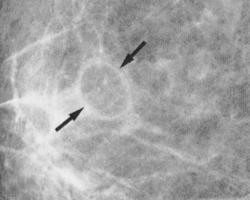 |
| Spiculated Lesions |  |
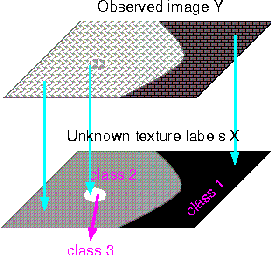 In the past several years there has been tremendous interest in image processing
and analysis techniques in mammography. One common approach for detecting
abnormalities in mammograms is to use a series of heuristics, e.g. filtering
and thresholding, which may include texture analysis to automatically detect
abnormalities. These heuristic methods suffer from a lack of robustness
when the number of images to be classified is large. Statistical
methods have also been developed to address this problem.
Our
new statistical algorithm partitions a mammogram into homogeneous texture
regions using random field model.
In the past several years there has been tremendous interest in image processing
and analysis techniques in mammography. One common approach for detecting
abnormalities in mammograms is to use a series of heuristics, e.g. filtering
and thresholding, which may include texture analysis to automatically detect
abnormalities. These heuristic methods suffer from a lack of robustness
when the number of images to be classified is large. Statistical
methods have also been developed to address this problem.
Our
new statistical algorithm partitions a mammogram into homogeneous texture
regions using random field model.
![]() M. L. Comer, S. Liu, E. J. Delp, "Statistical Segmentation of Mammograms,"
Proceedings of the 3nd International Workshop on Digital Mammography,
June 9-12,1996, Chicago, pp. 475-478.
The
readme file ,
compressed postscript file,
PDF file, and the
ftp site.
M. L. Comer, S. Liu, E. J. Delp, "Statistical Segmentation of Mammograms,"
Proceedings of the 3nd International Workshop on Digital Mammography,
June 9-12,1996, Chicago, pp. 475-478.
The
readme file ,
compressed postscript file,
PDF file, and the
ftp site.
 |
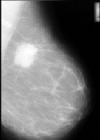 |
 |
![]() S. Liu, C. F. Babbs, and E. J. Delp
"Multiresolution Detection of Spiculated Lesions in Digital Mammograms,"
submitted to the IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,
The
readme
file,
compressed postscript file,
PDF file, and the
ftp site.
S. Liu, C. F. Babbs, and E. J. Delp
"Multiresolution Detection of Spiculated Lesions in Digital Mammograms,"
submitted to the IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,
The
readme
file,
compressed postscript file,
PDF file, and the
ftp site.
![]() S. Liu and E. J. Delp, "Multiresolution Detection of Stellate Lesions
in Mammograms,"
Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Image Processing,
October 26-29,1997, Santa Barbara, California, pp. II-109-II-112.
The
readme
file,
compressed postscript file,
PDF file, and the
ftp site.
S. Liu and E. J. Delp, "Multiresolution Detection of Stellate Lesions
in Mammograms,"
Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Image Processing,
October 26-29,1997, Santa Barbara, California, pp. II-109-II-112.
The
readme
file,
compressed postscript file,
PDF file, and the
ftp site.
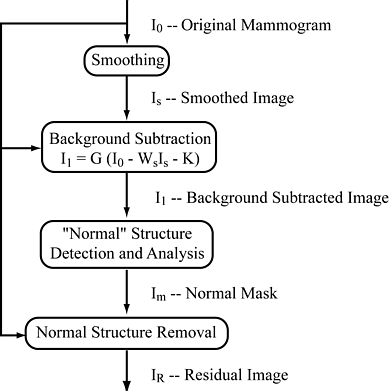 We propose a novel approach to the problem of computer aided
analysis of digital mammograms for breast cancer detection: namely, the
development of algorithms to recognize unequivocally normal mammograms.
The block diagram at right shows the normal tissue identification and removal
algorithm. We will refer to the mammogram that results from the removal of
normal structures as the residual image.
Any abnormality that
may exist in the mammogram is therefore enhanced in the residual image, which
makes the decision regarding the normality of the mammogram much easier.
We propose a novel approach to the problem of computer aided
analysis of digital mammograms for breast cancer detection: namely, the
development of algorithms to recognize unequivocally normal mammograms.
The block diagram at right shows the normal tissue identification and removal
algorithm. We will refer to the mammogram that results from the removal of
normal structures as the residual image.
Any abnormality that
may exist in the mammogram is therefore enhanced in the residual image, which
makes the decision regarding the normality of the mammogram much easier.
Eventually, the computer-aided diagnostic software would prescreen mammograms
with quantifiable high
accuracy and presents to the human reader a reduced number of more difficult
cases, together with the residual images. Hence it gives the human reader
both a reduced work load and extra clues or prompts, which would
improve his or her overall performance.
![]() S. Liu, C. F. Babbs, and E. J. Delp,
"Normal Mammogram Analysis and Recognition,"
Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing,
October 4-7,1998, Chicago, Illinois. The
readme
file,
compressed postscript file,
PDF file, and the
ftp site.
S. Liu, C. F. Babbs, and E. J. Delp,
"Normal Mammogram Analysis and Recognition,"
Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing,
October 4-7,1998, Chicago, Illinois. The
readme
file,
compressed postscript file,
PDF file, and the
ftp site.
Our recent publications in Medical Imaging and Image Analysis.
A complete set of recent publications at VIPER.