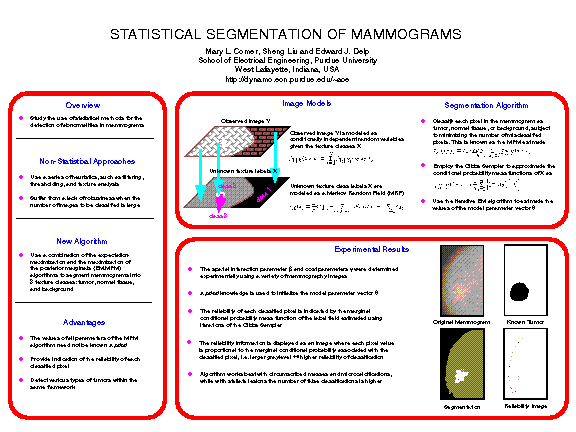
The following is a poster the authors presented at the 3rd International Workshop on Digital Mammography, 1996. To have a close look at the poster, please click on the area that interests you.
More detailed information may be found in:
![]() M. L. Comer, S. Liu, E. J. Delp, "Statistical Segmentation of Mammograms,"
Proceedings of the 3nd International Workshop on Digital Mammography,
June 9-12,1996, Chicago, pp. 475-478.
The
readme file ,
compressed postscript file,
PDF file, and the
ftp site.
M. L. Comer, S. Liu, E. J. Delp, "Statistical Segmentation of Mammograms,"
Proceedings of the 3nd International Workshop on Digital Mammography,
June 9-12,1996, Chicago, pp. 475-478.
The
readme file ,
compressed postscript file,
PDF file, and the
ftp site.