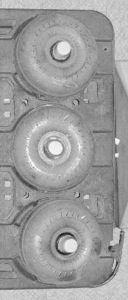
3D Vision for Torque Converter Localization
Localization of objects with few geometric features is a challenging problem for a computer vision system. Torque converters are very symmetric, round, and featureless and the system must localize within the error tolerance of 0.125 inch.
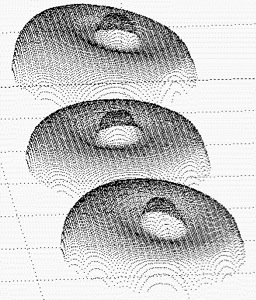
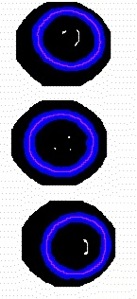
First, the system acquires 3D data points by using a structured-light scanning system. Given 3D data points of segmented torque converters, the system computes the approximate normal of each torque converter. Then, it extracts the coplanar points whose normals are within the boundary centered at the initial approximated normal. Then, it finds the largest connected region of coplanar points and generate skeleton image of the region through a thinning process. For each torque converter, the average (x, y, z) point of the skeleton image gives the center position and the best fitting plane of the skeleton image gives the orientation.