Overview
Summary
Deployed Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) experience conditions in the the physical world that are difficult to predict and test for during development. Even simulation and testbed deployment often fail to reveal every bug. The iterative processes of programing a deployed WSN, detecting failures, collecting information to diagnose the failures, and then re-programming the network, can be slow and laborious. It is also hampered by the parsimonious energy and resource constraints typical to WSNs. Our work focuses on the development of new software and hardware tools that provide a high level of visibility into deployed WSNs, while working within typical energy and resource constraints.
Achieved Technical Goals
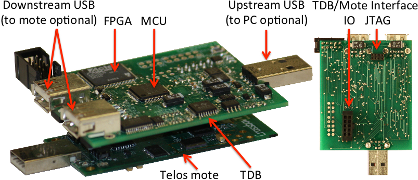
One outcome of our work is the Telos Debug Board (TDB), which is an implementation of Aveksha, our hardware-software approach for non-intrusively tracing and profiling sensor network motes. The TDB can be attached to a Telos mote and create a trace of events at a fine spatial or temporal granularity. It exploits the On-Chip Debug Module that is already embedded into the mote’s microcontroller chip. The advantage of this approach is that it is non-intrusive, meaning it does not affect the timing of a running application. This is important because some bugs may be masked by small changes in timing. A key aspect of the design is that the TDB is able to enter a low power sleep mode when the mote’s microcontroller goes to sleep. The TDB is easy to deploy because it does not require any change to mote’s hardware or software. The low power sleep functionality and ease of deployment makes the TDB suitable to debugging deployed WSNs.
Students
- Matthew Tan Creti, mtancret AT purdue DOT edu