|
|
|
|
At least
50% of
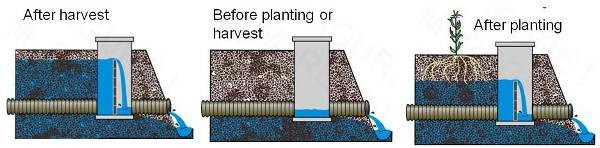
New in 2016 -- Agricultural Tile Drains Clogged With Cover Crop Roots?
|
|
Drainage and
Water Quality
Flow and nitrate leaching into tile drains
have been monitored for 15 years at the Southeast Purdue Agricultural
Center (SEPAC) experimental drainage plots. That web site provides
information on the level of nitrate carried by tile drains and reductions
that can be achieved when crop management practices are changed. Interpreting
Nitrate Concentration in Tile Drainage Water (AY 318-W, 8 pages, pdf)
provides general guidelines for interpreting measured NO3-N concentrations in drainflow samples collected through
monitoring programs, and describes the most important factors influencing
drainflow NO3-N concentrations. Drainage Water Management
Drainage
Water Management is a new practice in which water control
structures are installed in the main drain lines to hold water back and allow
farmers to drain only as needed.
·
Drainage Water
Management for the Midwest (WQ-44, 546
kB, pdf) This publication developed by researchers from 5 states answers
questions about drainage water management for the Midwest. ·
Narrated
powerpoint overview of drainage water management (4 minutes, presented by
Jane Frankenberger) Purdue
drainage water management research/demonstration project
Impacts of drainage water
management on nitrate loss, soil quality, and farm profitability are being
studied through paired-field trials on three private farms and a Purdue
University farm. Drain flow and nitrate concentration are being monitored in
each paired drainage water management ·
Overview
of Purdue project (narrated powerpoint, presented by Jane Frankenberger) ·
Drainage
Water Management Field Day at Davis-PAC - 2004. (Video of
Field Day (19:29), Handout from field day;
Photos from field day) |
Drain Spacing and Yield
Spacing
Recommendations Recommendations
for drainage depth and spacing in each soil type in Indiana based on years of
experience and knowledge of soil properties can be found in the publication
AY-300, Drainage Recommendations for Indiana Soils. See "Drainage
and Wet Soil Management" for more information and to download it as
a pdf file. Spacing Research
Data from Indiana research sites are
summarized in "Drainage
and Yield Studies" (actually part of a multi-state extension
publication posted at the Ohio State University site). Purdue Faculty with expertise in drainageDepartment
of Agronomy Eileen
Kladivko ( Department
of Agricultural and Biological Engineering Jane Frankenberger (frankenb@purdue.edu) |
|
For
more information on this Web site, contact Jane Frankenberger
(frankenb@purdue.edu) |