Radio navigation systems such as GPS, Beidou and Galileo have become one of the major solution for navigate around the world. Our lab have been involved with development of navigation solutions.
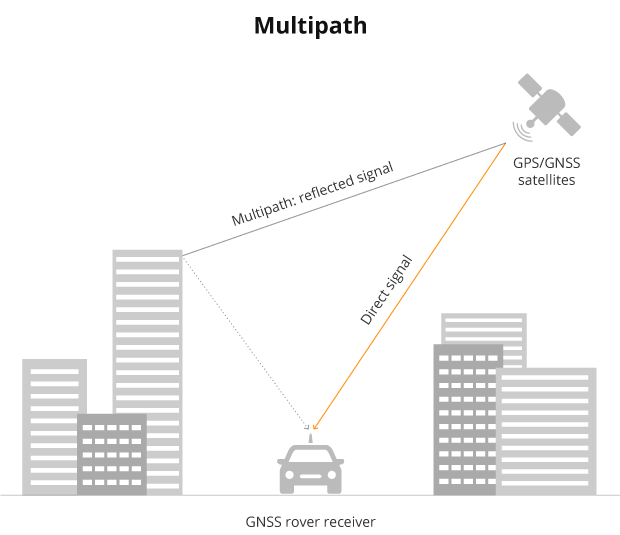
GPS multipath is a phenomenon that occurs when GPS signals bounce off surfaces such as buildings, mountains, or trees, and then arrive at the receiver’s antenna via multiple paths. This can cause the receiver to incorrectly calculate the distance between itself and the GPS satellites, leading to errors in the position estimate.
Multipath can be a problem for GPS receivers, especially in urban areas where there are many reflective surfaces. To reduce the impact of multipath, GPS receivers often use a technique called “multipath mitigation,” which involves filtering out or minimizing the effects of reflected signals.

By measuring the time delay between the received signals and the expected signals, the position of the satellite can be determined. This method is particularly useful for monitoring the position of geosynchronous satellites as it does not require specialized equipment or dedicated signals.
TIME DELAY OF ARRIVAL BASED ORBITDETERMINATION OF GEOSYNCHRONOUS SIGNALS OFOPPORTUNITY
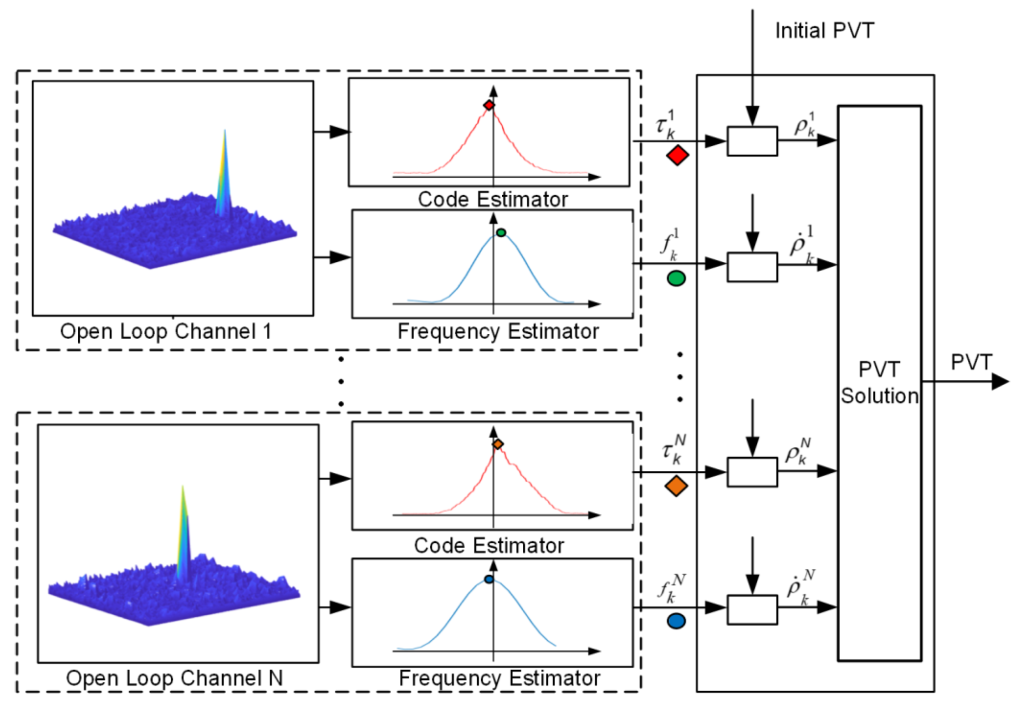
GNSS signal open-loop tracking is a technique used in Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) to track the phase and frequency of a satellite signal without using any feedback control.
Open loop tracking is often used in initial signal acquisition and also contains information on the atmosphere.
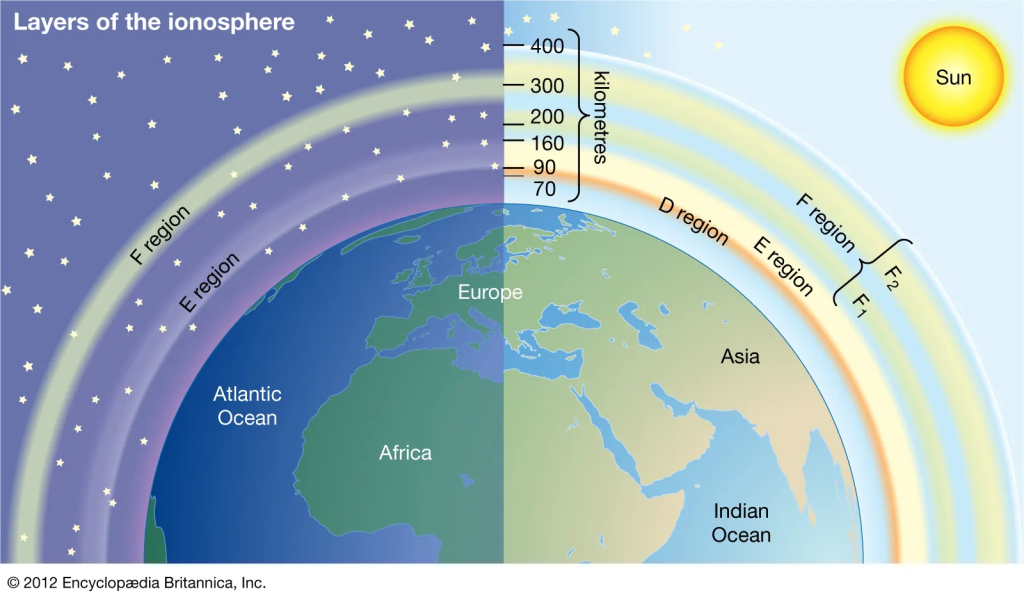
GPS Radio Occultation (GPS-RO) is an effective technique for measuring properties of the Earth’s atmosphere from space, and one that has demonstrated significant improvements in weather forecasts, climate modeling and space weather prediction.

