Signal of Opportunity (SoOp) ocean altimetry is a technique that uses signals from satellites in low Earth orbit, such as Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS), to measure sea surface height.
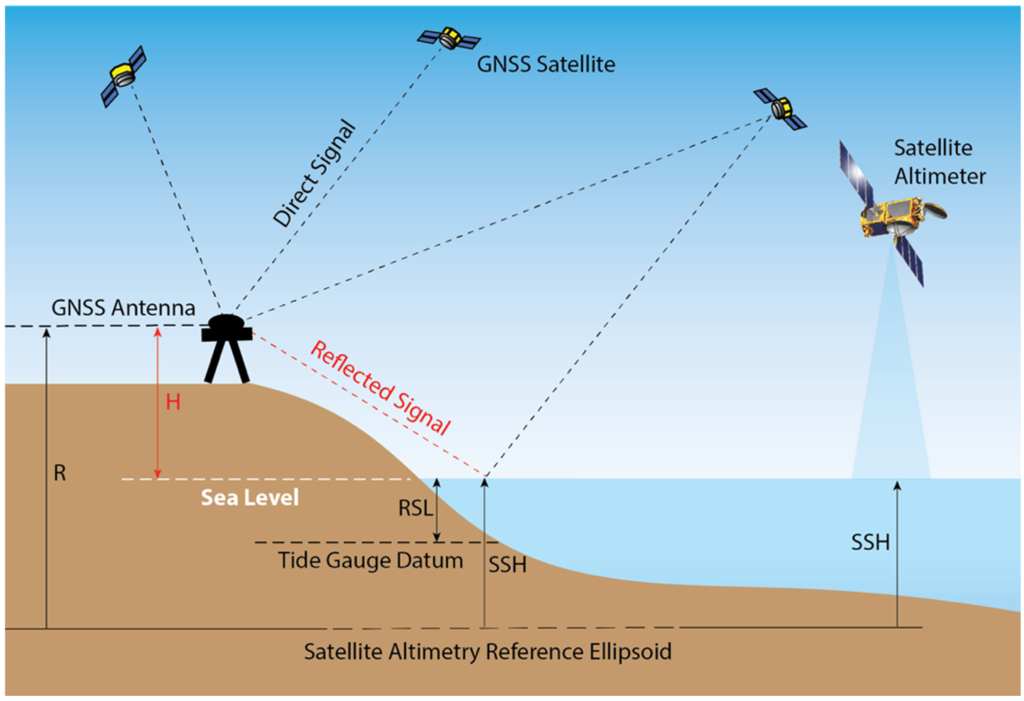
GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) ocean altimetry is a technique used to measure the height of the sea surface by analyzing the delay and phase shift of GNSS signals that are reflected from the ocean surface. This technique involves using GNSS signals from low Earth orbit satellites, such as GPS or Galileo, and analyzing the characteristics of the reflected signals to determine the distance between the satellite and the ocean surface.
By measuring the distance between the satellite and the ocean surface, GNSS ocean altimetry can provide information on ocean currents, tides, and sea level changes with high accuracy and spatial resolution. This technique has several advantages over traditional satellite altimetry, including lower costs, easier deployment, and higher temporal resolution.
WIDEBAND OCEAN ALTIMETRY USING KU AND K-BANDSATELLITE SIGNALS OF OPPORTUNITY (SOOP)

