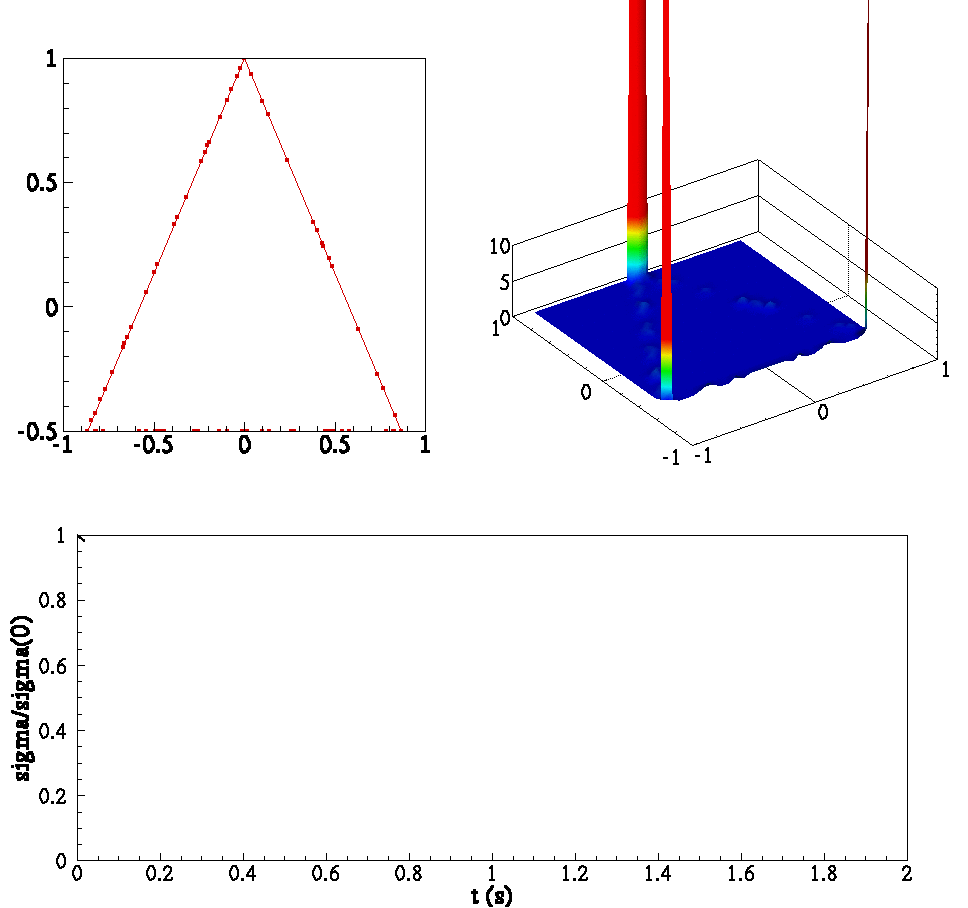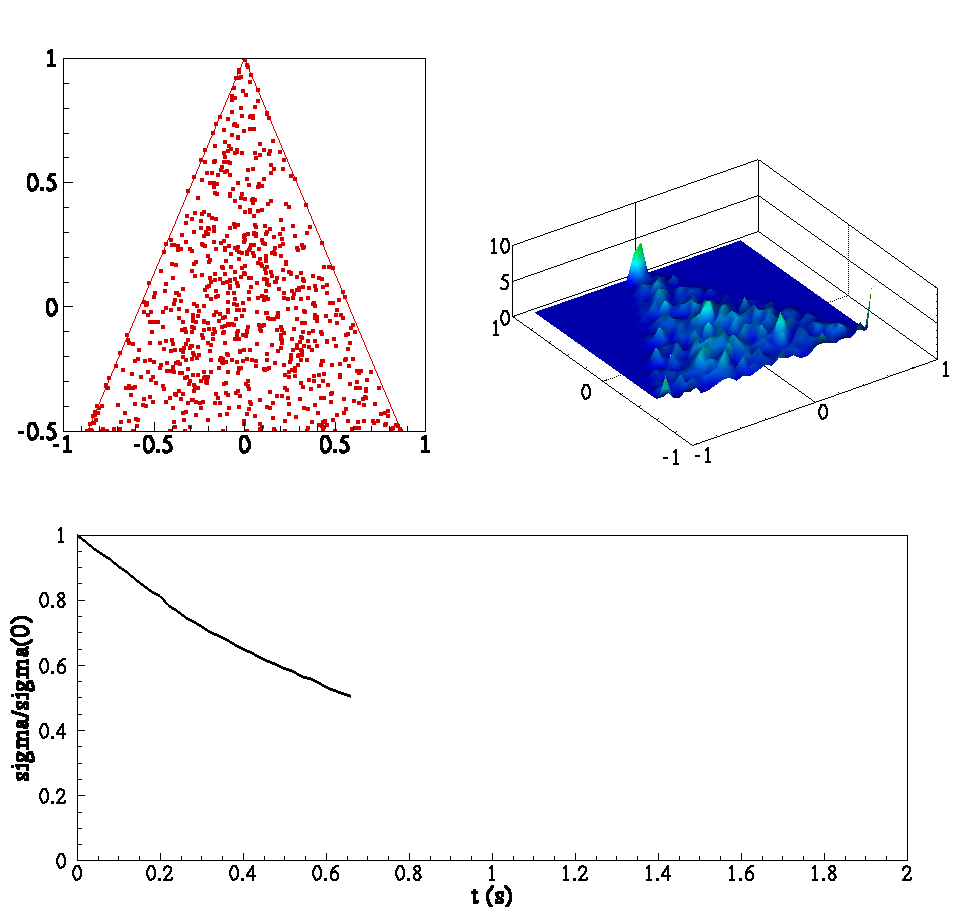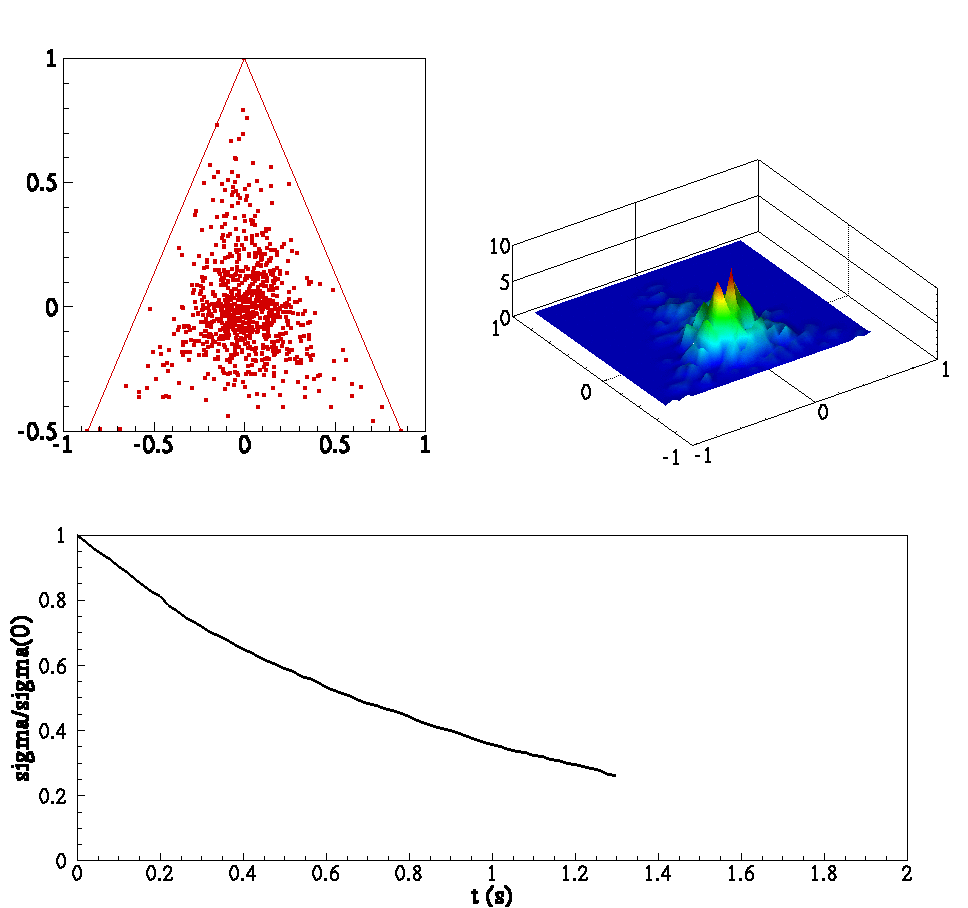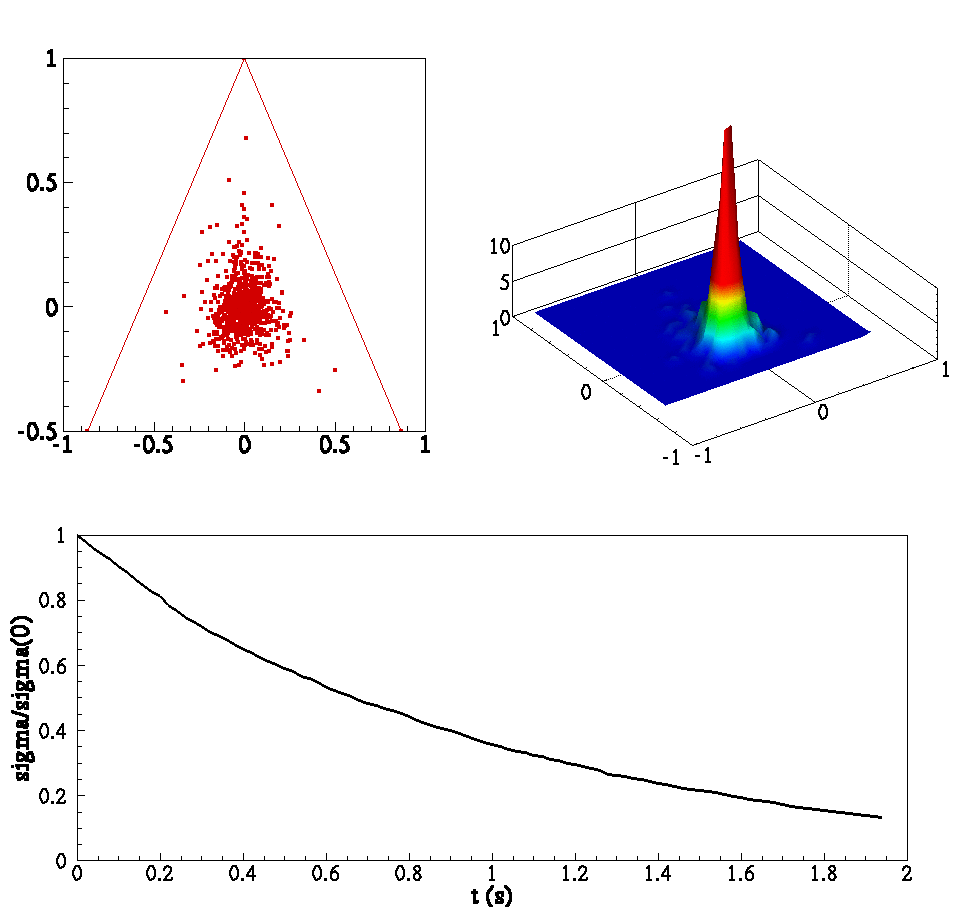
Investigation of Extinction and Reignition Phenomena in Turbulent Non-premixed Flames using PDF Methods
Joint PDF model in homogenous turbulence
Mixing models for closure of the scalar joint probability density function (jPDF)
in Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) or the scalar joint filtered density
function (jFDF) in Large Eddy Simulation (LES) often employ a constant mixing frequency
for all scalars and do not account for the effects of chemical reaction. This study
compares the performance of several different mixing models with regard to their ability
to predict three-stream mixing and nonpremixed flame extinction/reignition dynamics in
homogeneous turbulence. The mixing models considered include Interaction by Exchange with
the Mean (IEM), the Modified Curl (MC), the Euclidean Minimum Spanning Tree (EMST), and
the method of Multiple Mapping Conditioning (MMC) (the latter only in the context of pure
mixing). The jPDF predictions from the different mixing models are compared to results
obtained from Linear Eddy Model (LEM) simulations.
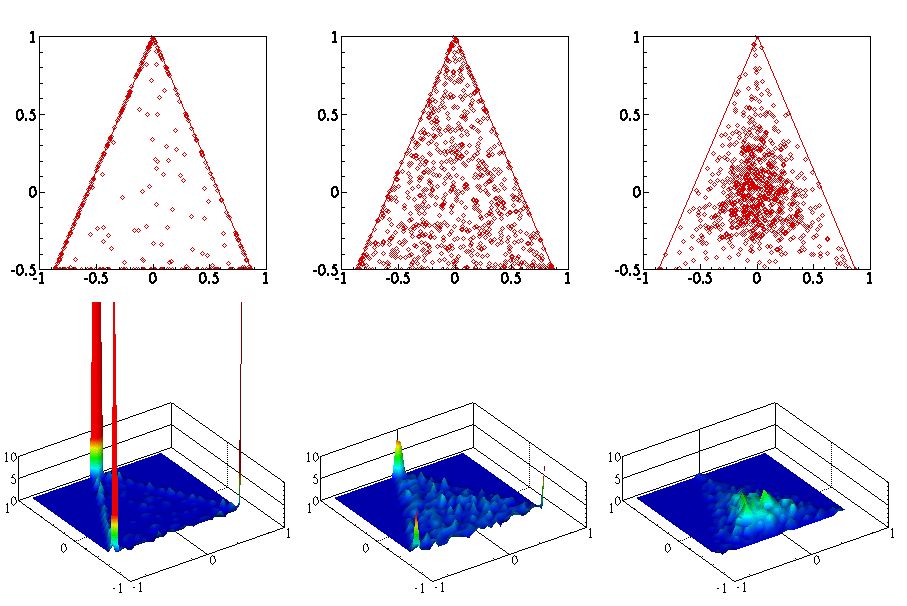
Below is an animation of (clockwise from left) (1) particles in a box colored by temperature (2) joint PDF of reactants (3) joint PDF of reactant and product (4) Evolution of scalar means and (5) evolution of PDF conditioned on stoichiometric.