 |
-
Technologies for Minaiture MS
- Miniature MS Instruments
- Performance and Applications of Miniature MS
|
|
| |
|
DAPI - Discontinuous Atmospheric Pressure Interface
- Breaking the pumping speed barrier in Mass Spectrometry
|
|
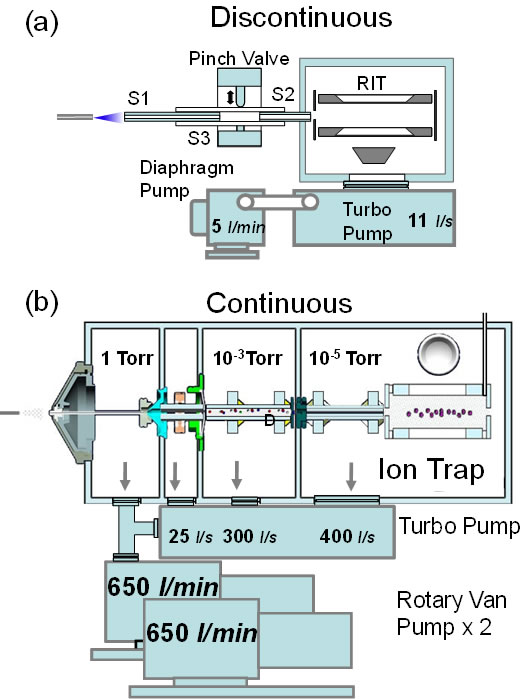 The performance of mass spectrometers with limited pumping capacity is shown to be improved through use of a discontinuous atmospheric pressure interface (DAPI). A proof-of-concept DAPI interface was designed and characterized using a miniature rectilinear ion trap mass spectrometer. The interface consisted of a simple capillary directly connecting the atmospheric pressure ion source to the vacuum mass analyzer region; it has no ion optical elements and no differential pumping stages. Gases carrying ionized analytes were pulsed into the mass analyzer for short periods at high flow rates rather than being continuously introduced at lower flow rates; this procedure maximized ion transfer. The use of DAPI provides a simple solution to the problem of coupling an atmospheric pressure ionization source to a miniature instrument with limited pumping capacity. The performance of mass spectrometers with limited pumping capacity is shown to be improved through use of a discontinuous atmospheric pressure interface (DAPI). A proof-of-concept DAPI interface was designed and characterized using a miniature rectilinear ion trap mass spectrometer. The interface consisted of a simple capillary directly connecting the atmospheric pressure ion source to the vacuum mass analyzer region; it has no ion optical elements and no differential pumping stages. Gases carrying ionized analytes were pulsed into the mass analyzer for short periods at high flow rates rather than being continuously introduced at lower flow rates; this procedure maximized ion transfer. The use of DAPI provides a simple solution to the problem of coupling an atmospheric pressure ionization source to a miniature instrument with limited pumping capacity.
Data were recorded using various atmospheric pressure ionization sources, including electrospray ionization (ESI), nano-ESI, atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) and desorption electrospray ionization (DESI) sources. The interface was opened briefly for ion introduction during each scan. Using the 18 W pumping system of the Mini 10, limits of detection in the low ppb levels were achieved and unit resolution mass spectra were recorded.
Figure: Schematics of vacuum systems for a) a handheld mass spectrometer using discontinuous atmospheric pressure interface (DAPI) and b)
- Liang Gao, R. Graham Cooks, Zheng Ouyang, "Breaking the Pumping Speed Barrier in Mass Spectrometry: Discontinuous Atmospheric Pressure Interface" , Analytical Chemistry , 2008 , 80, 4026-4032, doi:10.1021/ac800014v
|
|
| |
|
Backpack Mini MS with a DAPI Sampling Probe
|
|
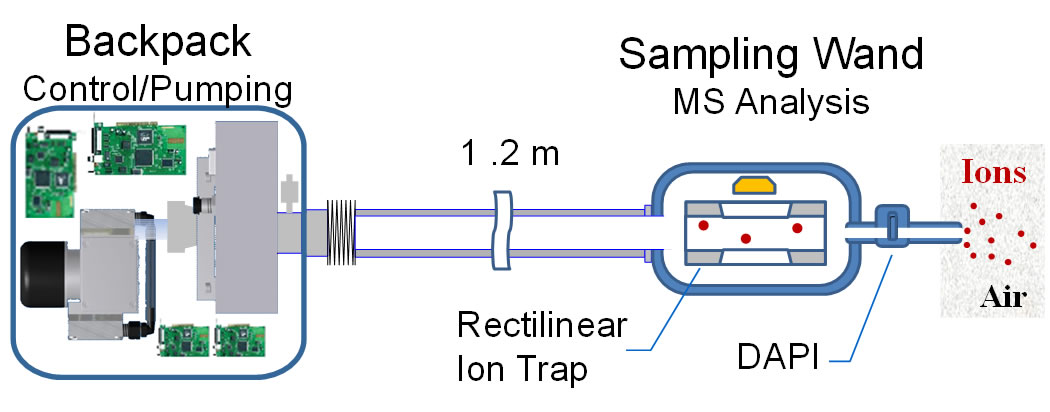 A theoretical modeling method was explored for characterizing the ion transient response to a dipolar AC excitation A new sampling wand concept for ion trap mass spectrometers equipped with discontinuous atmospheric pressure interfaces (DAPI) has been implemented. The ion trap/DAPI combination facilitates the operation of miniature mass spectrometers equipped with ambient ionization sources. However, in the new implementation, instead of transferring ions pneumatically from a distant source, the mass analyzer and DAPI are separated from the main body of the mass spectrometer and installed at the end of a 1.2 m long wand. During ion introduction, ions are captured in the ion trap while the gas in which they are contained passes through the probe and is pumped away. The larger vacuum volume due to the extended wand improves the mass analysis sensitivity. The wand was tested using a modified handheld ion trap mass spectrometer without additional power or pumping required. Improved sensitivity was obtained as demonstrated with nano-ESI, atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI), and low temperature plasma (LTP) probe analysis of liquid, gaseous and solid samples, respectively. A theoretical modeling method was explored for characterizing the ion transient response to a dipolar AC excitation A new sampling wand concept for ion trap mass spectrometers equipped with discontinuous atmospheric pressure interfaces (DAPI) has been implemented. The ion trap/DAPI combination facilitates the operation of miniature mass spectrometers equipped with ambient ionization sources. However, in the new implementation, instead of transferring ions pneumatically from a distant source, the mass analyzer and DAPI are separated from the main body of the mass spectrometer and installed at the end of a 1.2 m long wand. During ion introduction, ions are captured in the ion trap while the gas in which they are contained passes through the probe and is pumped away. The larger vacuum volume due to the extended wand improves the mass analysis sensitivity. The wand was tested using a modified handheld ion trap mass spectrometer without additional power or pumping required. Improved sensitivity was obtained as demonstrated with nano-ESI, atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI), and low temperature plasma (LTP) probe analysis of liquid, gaseous and solid samples, respectively.
- K. Y. Hou, W. Xu, J. A. Xu, R. G. Cooks and Z. Ouyang, "Sampling Wand for an Ion Trap Mass Spectrometer", Analytical Chemistry, 2011, 83, 1857-1861, DOI: 10.1021/ac102962e
|
|